A) displacement
B) rotation
C) internal strain of the rock
D) columnar joints
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What causes the stress that forms joints?
A) burial and tectonic forces
B) cooling and contraction
C) uplift and unloading of pressure
D) All of these
E) None of these
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of eruption is shown in this photograph? 
A) lava flow
B) lava dome
C) lava fountain
D) pyroclastic column
E) pyroclastic flow
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fractures along which the rock has slipped relative to the other side are called
A) faults.
B) cracks.
C) joints.
D) beds.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The igneous feature shown in this figure is a 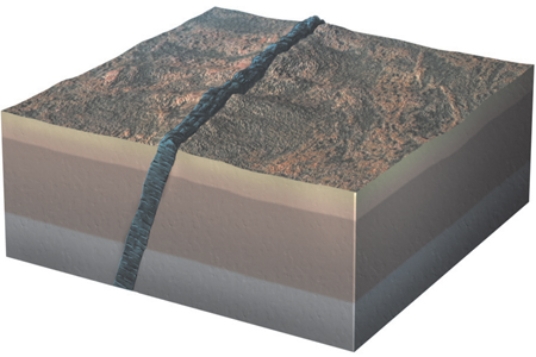
A) dike.
B) sill.
C) volcanic neck.
D) laccolith.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Folds are most often created through what type of stress?
A) compression
B) tension
C) shear
D) confining
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comparing these two photographs, which eruption has lower viscosity magma? 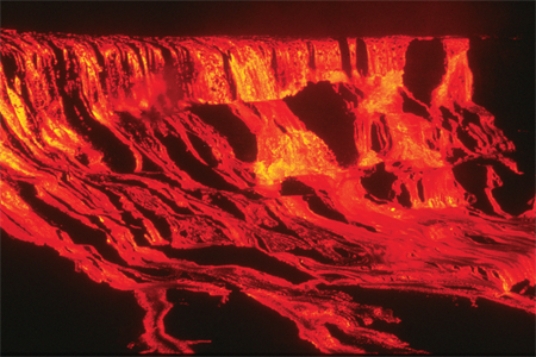

A) the fluid cascade of lava
B) the circular volcanic feature
C) they could have the same viscosity
D) there is no way to tell
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cannot cause a tsunami?
A) faulting
B) an underwater landslide
C) a volcanic eruption
D) a strike-slip fault on land
E) All of these can cause a tsunami.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On this map of South America and adjacent areas, which site would have the deepest earthquakes? 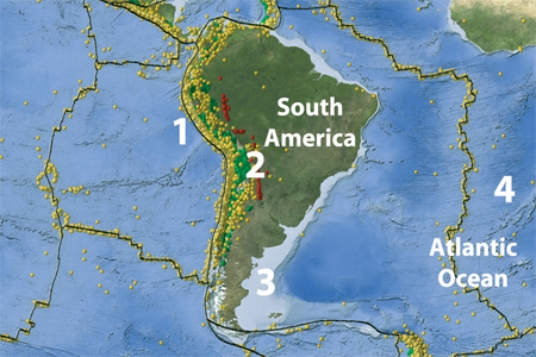
A) 1, the oceanic trench
B) 2, below the magmatic belt
C) 3, along a passive margin
D) 4, in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean
E) Both 1 and 2.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How would the force and stress on the wooden pillar in this figure change if the stone weight was the same size but the wooden pillar was narrower? 
A) The amount of force and amount of stress would be unchanged.
B) The amount of force and the amount of stress would both increase.
C) The amount of force and the amount of stress would both decrease.
D) The force would remain the same, but the amount of stress would increase.
E) The force would remain the same, but the amount of stress would decrease.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The typical shape of most volcanoes is
A) conical.
B) cylindrical.
C) domical.
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of evidence was used in the Investigation to locate where the earthquake occurred?
A) photographs showing the amount of damage in different places
B) newspaper accounts of where buildings were destroyed
C) newspaper accounts recording eyewitness observations
D) seismograms from three stations
E) All of these.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relatively small volcanic feature that consists of solidified lava and some volcanic ash is a
A) cinder cone.
B) shield volcano.
C) composite volcano.
D) caldera.
E) None of these.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are NOT differences between an eruption column and pyroclastic flow?
A) Tephra in an eruption column mostly cools before it reaches the ground.
B) A pyroclastic flow mostly flows downhill, whereas a column rises at first.
C) Damage from an eruption column can be more widespread.
D) Pyroclastic flows form from a higher gas flux.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Shield volcanoes have low slopes primarily because
A) the low viscosity of basaltic magma allows it to flow downhill for long distances.
B) they never erupt from the same place twice.
C) their abundant ash layers spread out large distances.
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are ways that viscosity affects gases in magma?
A) Viscous magma prevents gas from escaping easily.
B) Abundant silica chains in viscous magma allow gas to pass quickly through the magma.
C) Less viscous magma allows gas to escape, which can lead to very explosive eruptions.
D) All of these.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most dangerous type of volcano is a
A) cinder cone.
B) cinder cone whose magmas are interacting with groundwater.
C) huge shield volcano.
D) composite volcano.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a way in which local mountains can be built?
A) prolonged volcanism in composite volcanoes
B) thrust faulting
C) normal faulting
D) folding
E) All of these are ways to make local mountains.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are true for horsts and grabens?
A) A horst is a block that is uplifted relative to blocks on either side.
B) A graben is a block that is dropped down relative to blocks on either side.
C) May form associated with multiple normal faults.
D) These are all true of horsts and grabens.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An earthquake generated on this type of fault would most likely be associated with a 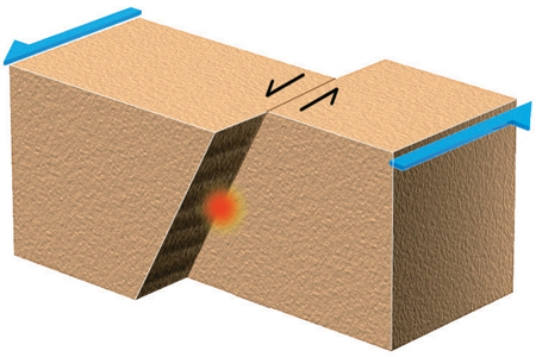
A) subduction zone.
B) divergent plate boundary.
C) rift.
D) caldera.
E) transform boundary.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 218
Related Exams