A) joint.
B) normal fault.
C) reverse fault.
D) strike-slip fault.
E) dip-slip fault.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are characteristics of actively erupting volcanoes? 
A) Glowing orange lava flowing downhill.
B) Fragments of molten rock blasting into the air.
C) Billowing clouds of ash rising into the air.
D) All of these.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is common in most calderas?
A) a large circular depression with steep walls
B) thick sequences of volcanic ash
C) rounded mountains that are volcanic domes
D) All of these.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sudden movement on a fault can cause a tsunami when
A) a hurricane or cyclone is occurring.
B) the fault suddenly uplifts or downdrops the seafloor.
C) hot water trapped below the seafloor is released.
D) a fault on land has a large displacement.
E) None of these.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a hazard but not a risk, according to the textbook?
A) the Kilauea volcano, which covers subdivisions with molten lava
B) a cinder cone that erupts hot molten fragments on an unpopulated Pacific island
C) a volcano in Iceland that threatens people with dangerous gases
D) a volcano in Iceland that caused catastrophic flooding that destroyed houses and roads
E) All of these are both a hazard and a risk.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT evidence of recent activity at a volcano?
A) thick, well-developed soil
B) layer of ash blanketing hillslopes
C) unweathered lava flows
D) ash flows lacking a well-developed soil
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following was NOT associated with the Alaskan earthquake of 1964?
A) destruction of houses when a layer of weak clay liquefied
B) landslides generated from steep mountainsides
C) sinking of some downtown buildings by several meters
D) a tsunami that killed people in Oregon and California
E) a large strike-slip fault
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do the two stars near the center of this block represent? 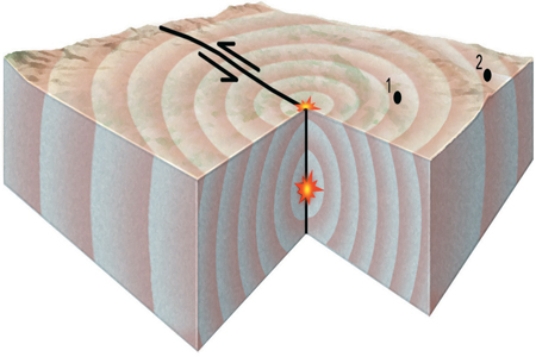
A) the location of the earthquake
B) the star at depth is the place where the earthquake is generated
C) the star at depth is the hypocenter
D) the star on the surface is the epicenter
E) All of these.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The typical form for a composite volcano is a
A) steep-sided cone.
B) shallowly-sloping shield.
C) broad, circular crater.
D) steep-sided dome.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of structure shown in this figure is a(n) 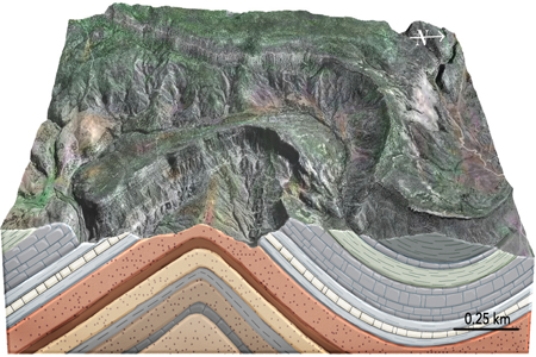
A) thrust fault.
B) anticline.
C) syncline.
D) monocline.
E) dome.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a main hazard of this type of volcano? 
A) hot molten fragments thrown a short distance from the volcano
B) viscous lava that moves too fast for people to outrun
C) destruction by moderately fluid lava flows that can flow far from the volcano
D) relatively small pyroclastic eruptions caused by localized explosions or collapse
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following features was most likely the cause of the earthquake in the Investigation?
A) oceanic trench
B) collapse of hills along the shoreline
C) faulting along a line of cliffs
D) a landslide off Red Mesa
E) earthquakes from within Lava Mountain
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most common volcanic rock found in lava flows on composite volcanoes is
A) andesite.
B) basalt.
C) obsidian.
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the temperature of materials typically erupted from volcanoes?
A) extremely hot
B) warm to slightly hot
C) cool to cold
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of volcanic eruption shown in this photograph is 
A) a lava fountain.
B) collapse of a volcanic dome.
C) a fissure eruption.
D) a pyroclastic column.
E) a volcanic mudflow.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a way that volcanoes and magma can cause earthquakes?
A) Volcanic explosions cause seismic waves.
B) Volcanoes can load the crust, causing faulting and earthquakes.
C) Many volcanoes have steep, unstable slopes that can cause landslides that shake the ground.
D) Moving magma within or below the volcano can cause earthquakes.
E) All of these are ways that volcanoes can cause earthquakes.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Eruptions on the island of Santorini in Greece resulted in
A) collapse of a huge caldera that caused part of an island to disappear beneath the sea.
B) a huge ash column and pyroclastic flows.
C) destructive waves that traveled across the sea.
D) All of these.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If bubbles cannot escape easily from a magma, the resulting eruption is likely to
A) be explosive.
B) be nonexplosive.
C) produce long, thin lava flows.
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 218 of 218
Related Exams