A) Severe ground shaking that damaged buildings near the earthquake
B) A deadly tsunami
C) Destruction of a nuclear power plant
D) All of these are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of fault shown in this figure is a 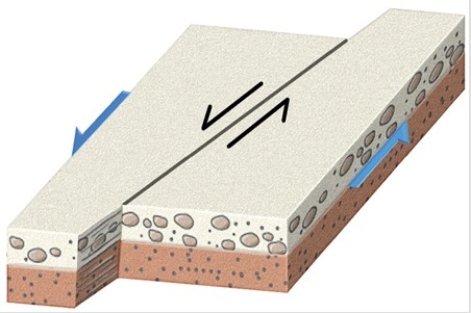
A) dip-slip fault.
B) normal fault.
C) strike-slip fault.
D) reverse fault.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of volcanic eruption is probably shown in this photograph? 
A) Fire fountain
B) Basaltic lava flow
C) Felsic lava flow
D) Caldera eruption
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a major source of earthquakes associated with continental collisions?
A) Thrust faults
B) Slip along the plate boundary
C) Faulting in a wide area adjacent to the collision zone
D) All of these are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Shield volcanoes have low slopes primarily because
A) the low viscosity of basaltic magma allows it to flow downhill for long distances.
B) they never erupt from the same place twice.
C) their abundant ash layers spread out large distances.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a way in which volcanic domes are commonly destroyed?
A) collapse into emptied magma chambers below
B) collapse of steep flanks into block and ash flows
C) internally derived explosions from built-up gas pressure
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following was common to the eruptions of Vesuvius and Mount St.Helens?
A) Both are composite volcanoes
B) Earthquakes before the eruption
C) Small eruptions of tephra
D) Pyroclastic flows
E) All of these are correct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an earthquake occurred near the oceanic trench in this figure,which one of the following hazards is likely to threaten the town of Ashton? 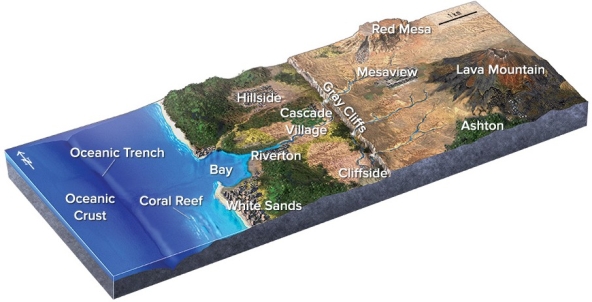
A) Destruction by a tsunami
B) Liquefaction of soils and other weak materials because of shaking
C) Landslides and other slope failures caused by shaking
D) All of these are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A single volcano may produce
A) only explosive eruptions.
B) only nonexplosive eruptions.
C) both explosive and nonexplosive eruptions.
D) either explosive or nonexplosive eruptions,but never both.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a location in which flood basalts erupted?
A) Columbia Plateau
B) Texas Gulf Coast
C) Hawaii
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following sites would most likely have composite volcanoes? A is on an island arc,B is in the Andes,C is near Hawaii,D is along a midocean ridge. 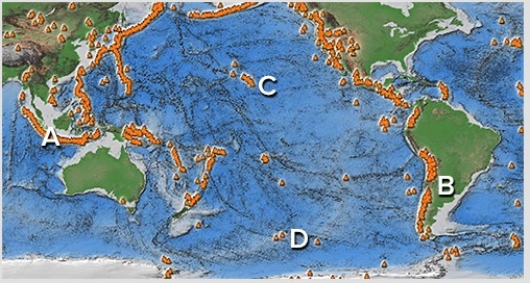
A) A and B
B) B and C
C) C and D
D) A and C
E) B and D
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Earthquakes at Mount St.Helens prior to the major eruption in 1980 were caused by
A) magma rising in the volcano.
B) tectonic plate movement.
C) landslides.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of evidence was used in the Investigation to locate where the earthquake occurred?
A) Photographs showing the amount of damage in different places
B) Newspaper accounts of where buildings were destroyed
C) Newspaper accounts recording eyewitness observations
D) Seismograms from three stations
E) All of these are correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At what depth do gas bubbles have the most effect on magma?
A) When the magma first forms,before the bubbles can dissolve into the magma
B) At moderate depths,when the magma is moving rapidly through the conduit
C) At very shallow levels,such as within the volcano
D) None of these are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Steep-sided hills of viscous lava that pile up over volcanic vents are known as
A) volcanic domes.
B) cinder cones.
C) composite volcanoes.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the strength of continental crust vary with depth?
A) Rocks become stronger with depth and then get weaker deep in the crust.
B) Rocks weaken with depth and then get stronger deep in the crust.
C) Rocks systematically get stronger from the surface to deep in the crust.
D) Rocks systematically get weaker from the surface to deep in the crust.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most dangerous type of volcano is a
A) cinder cone.
B) cinder cone whose magmas are interacting with groundwater.
C) huge shield volcano.
D) composite volcano.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The dark igneous features shown in this photograph are 
A) dikes.
B) sills.
C) volcanic necks.
D) batholiths.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are ways that viscosity affects gases in magma?
A) Viscous magma prevents gas from escaping easily.
B) Abundant silica chains in viscous magma allow gas to pass quickly through the magma.
C) Less viscous magma allows gas to escape,which can lead to very explosive eruptions.
D) All of these are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a way that volcanoes and magma can cause earthquakes?
A) Volcanic explosions cause seismic waves.
B) Volcanoes can load the crust,causing faulting and earthquakes.
C) Many volcanoes have steep,unstable slopes that can cause landslides that shake the ground.
D) Moving magma within or below the volcano can cause earthquakes.
E) All of these are ways that volcanoes can cause earthquakes.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 218
Related Exams