A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When can the z-test be used in statistical hypothesis testing?
A) When the measure of central tendency used for the raw scores is the median
B) When the raw scores are transformed from a nominal scale to a ratio scale
C) When the raw score population's standard deviation is known
D) When the z-test standard deviation is known
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does alpha always represent in statistical hypothesis testing?
A) The probability of making a correct decision about ![]()
B) The relative size of the region of rejection
C) The critical value
D) 0.05
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens when the experimental results are nonsignificant?
A) The alternative hypothesis has been accepted.
B) The alternative hypothesis has been rejected.
C) The null hypothesis has been rejected.
D) The null hypothesis has not been rejected.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a one-tailed test where the predicted value of the sample mean is larger than the population mean and = 0.05, 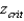 is always equal to
is always equal to
A) ±1.645.
B) +1.645.
C) 1.645.
D) ±1.96.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does it mean when a computer printout reads "p = 0.03"?
A) The ![]() falls in the extreme 3% of the sampling distribution and the probability of a Type I error is 0.03.
falls in the extreme 3% of the sampling distribution and the probability of a Type I error is 0.03.
B) The ![]() falls in the extreme 3% of the sampling distribution and the probability of a Type II error is 0.03.
falls in the extreme 3% of the sampling distribution and the probability of a Type II error is 0.03.
C) The probability of a Type I error (0.03) is smaller than (0.05) ,and,therefore,the results are nonsignificant.
D) The probability of an error should be reported as p 0.01.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following tests is considered to be more powerful?
A) A one-tailed test
B) A two-tailed test
C) Neither;they are both equally statistically powerful
D) Which is more powerful depends on the sample size
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When is a one-tailed test used?
A) When no relationship is predicted
B) When a relationship is predicted and the direction in which the scores will change is predicted
C) When the demonstrated relationship is predicted
D) When a relationship is predicted without stating the direction in which the scores will change
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following assumptions is common to all parametric statistics?
A) There are no common assumptions.
B) The population of dependent scores,regardless of what kind of scores they are,forms a normal distribution.
C) The dependent scores must be interval or ratio scores,regardless of whether the population of scores forms a normal distribution.
D) The population of dependent scores,which must be interval or ratio scores,forms a normal distribution.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does the sampling distribution describe?
A) The sample distribution when the null hypothesis is true.
B) The sampling distribution when the null hypothesis is true.
C) The population distribution when the null hypothesis is false.
D) The alternative distribution when the null hypothesis is false.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In using a sampling distribution of means for statistical hypothesis testing,the mean of the sampling distribution will always equal
A) the µ described by ![]() .
.
B) the µ described by ![]() .
.
C) the sample mean.
D) 0.0.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a two-tailed test where = 0.05, 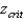 is always equal to
is always equal to
A) 1.96.
B) +1.96.
C) ±1.96.
D) ±1.645.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens to the probability of committing a Type I error if the level of significance is changed from = 0.01 to = 0.05?
A) The probability of committing a Type I error will decrease.
B) The probability of committing a Type I error will increase.
C) The probability of committing a Type I error will remain the same.
D) The change in probability will depend on your sample size.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a one-tailed test 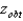 is significant only if it lies
is significant only if it lies
A) nearer ![]() than
than![]() and has a different sign from
and has a different sign from![]() .
.
B) in the tail of the distribution beyond ![]() and has a different sign from
and has a different sign from![]() .
.
C) nearer ![]() than
than![]() and has the same sign as
and has the same sign as![]() .
.
D) in the tail of the distribution beyond ![]() and has the same sign as
and has the same sign as![]() .
.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The null hypothesis describes the
A) sample statistic and the region of rejection.
B) sample statistic if a relationship does not exist in the sample.
C) population parameters represented by the sample data if the predicted relationship exists.
D) population parameters represented by the sample data if the predicted relationship does not exist.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is called the hypothesis of "no difference"?
A) The null hypothesis
B) The experimental hypothesis
C) The alternative hypothesis
D) The statistical hypothesis
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the null hypothesis,if our 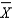 appears to represent the predicted relationship,it is because
appears to represent the predicted relationship,it is because
A) the relationship actually exists.
B) our sample is invalid.
C) something has gone terribly wrong.
D) of sampling error.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct regarding the probability of making a Type I error?
A) p =
B) p = (1 )
C) p <
D) p >
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When is a two-tailed test used?
A) When no relationship is predicted
B) When a relationship is predicted and the direction in which the scores will change is predicted
C) When the demonstrated relationship is predicted
D) When a relationship is predicted without stating the direction in which the scores will change
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following accurately defines a Type I error?
A) Rejecting ![]() when
when![]() is true
is true
B) Rejecting ![]() when
when![]() is false
is false
C) Retaining ![]() when
when![]() is true
is true
D) Retaining ![]() when
when![]() is false
is false
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 56
Related Exams