A) a sturdy-finned, shallow-water lobe-fin whose appendages had skeletal supports similar to those of terrestrial vertebrates
B) an armored gnathostome with two pairs of appendages
C) an early ray-finned fish that developed bony skeletal supports in its paired fins
D) a salamander that had legs supported by a bony skeleton but moved with the side-to-side bending typical of fishes
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The earliest known mineralized structures in vertebrates are associated with which function?
A) reproduction
B) feeding
C) locomotion
D) defense
E) respiration
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the evidence collected so far, the animal kingdom is
A) monophyletic.
B) paraphyletic.
C) no longer growing in size.
D) growing at an exponential rate.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of members of the phylum Cnidaria?
A) They are not capable of locomotion because they lack true muscle tissue.
B) They are primarily filter feeders.
C) They coordinate movements through a noncentralized nerve set.
D) They are the simplest organisms with a complete alimentary canal (two openings) .
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. An elementary school science teacher decided to liven up the classroom with a saltwater aquarium. Knowing that saltwater aquaria can be quite a hassle, the teacher proceeded stepwise. First, the teacher conditioned the water. Next, the teacher decided to stock the tank with various marine invertebrates, including a sea star, a sponge, a sea urchin, a jellyfish, several hermit crabs, some sand dollars, and an ectoproct. Last, she added some vertebrates - a parrotfish and a clownfish. She arranged for daily feedings of copepods and feeder fish. -Had the teacher wanted to point out organisms that move and feed using the same structural adaptation, the teacher should have chosen the
A) sponge and the jellyfish.
B) hermit crabs and the ecotoprot.
C) sea star, sea urchin, and sand dollars.
D) vertebrates.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If all of the animals died in a large region of an ocean, we would expect an increase in the
A) number of filter feeders.
B) number of cyanobacteria.
C) number of decomposers.
D) clarity of the ocean waters.
E) temperature of the ocean waters.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Trichoplax adhaerens (Tp) is the only living species in the phylum Placozoa. Individuals are about 1 mm wide and only 27 μm high, are irregularly shaped, and consist of a total of about 2,000 cells, which are diploid (2n = 12) . There are four types of cells, none of which is a nerve or muscle cell, and none of which has a cell wall. They move using cilia, and any "edge" can lead. Tp feeds on marine microbes, mostly unicellular green algae, by crawling atop the algae and trapping it between its ventral surface and the substrate. Enzymes are then secreted onto the algae, and the resulting nutrients are absorbed. Tp sperm cells have never been observed, nor have embryos past the 64-cell (blastula) stage. -In which of the following ways is Tp similar to a typical animal? 1) Tp is multicellular. 2) Tp lacks muscle and nerve cells. 3) Tp has cilia. 4) Tp lacks cell walls. 5) Tp does not have observable sperm cells.
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 1, 3, and 5 only
D) 3, 4, and 5 only
E) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The decline of cyanobacteria in the early Cambrian oceans was most likely related to
A) the movement of animals onto land.
B) the evolution of land plants.
C) an increase in the number of predatory fish.
D) an increase in organisms with suspension-feeding mouthparts.
E) a decline in the number of marine decomposers.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. The most recently discovered phylum in the animal kingdom (1995) is the phylum Cycliophora. It includes three species of tiny organisms that live in large numbers on the outsides of the mouthparts and appendages of lobsters. When in the feeding stage, a cycliophoran permanently attaches to the lobster via an adhesive disk and collects scraps of food from its host's feeding by capturing the scraps in a current created by a ring of cilia. Its body is sac-like and has a U-shaped intestine that brings the anus close to the mouth. Cycliophorans are eucoelomate (have a body cavity that is a coelom) and do not molt (though their host does) . -What is true of the feeding stage of cycliophorans? 1) It is chemoheterotrophic. 2) It is sessile. 3) Its tube feet allow it to feed efficiently. 4) It has radial symmetry.
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 2, and 3 only
E) 2, 3, and 4 only
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A trend first observed in the evolution of the earliest tetrapods was
A) the appearance of jaws.
B) the appearance of bony vertebrae.
C) feet with digits.
D) the mineralization of the endoskeleton.
E) the amniotic egg.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
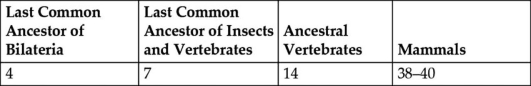 Table 27.1. Proposed Number of Hox Genes in Various Extant and Extinct Animals
-What conclusion is apparent from the data in Table 27.1?
Table 27.1. Proposed Number of Hox Genes in Various Extant and Extinct Animals
-What conclusion is apparent from the data in Table 27.1?
A) Land animals have more Hox genes than do those that live in water.
B) All bilaterian phyla have had the same degree of expansion in their numbers of Hox genes.
C) Acoel flatworms should be expected to contain seven Hox genes.
D) The expansion in number of Hox genes throughout vertebrate evolution cannot be explained merely by three duplications of the ancestral vertebrate Hox cluster.
E) Extant insects all have seven Hox genes.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Trichoplax adhaerens (Tp) is the only living species in the phylum Placozoa. Individuals are about 1 mm wide and only 27 μm high, are irregularly shaped, and consist of a total of about 2,000 cells, which are diploid (2n = 12) . There are four types of cells, none of which is a nerve or muscle cell, and none of which has a cell wall. They move using cilia, and any "edge" can lead. Tp feeds on marine microbes, mostly unicellular green algae, by crawling atop the algae and trapping it between its ventral surface and the substrate. Enzymes are then secreted onto the algae, and the resulting nutrients are absorbed. Tp sperm cells have never been observed, nor have embryos past the 64-cell (blastula) stage. -Tp's body symmetry seems to be most like that of
A) most sponges.
B) cnidarians.
C) worms.
D) tetrapods.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure given below, the Deuterostomia clade is most closely related to which two main clades? 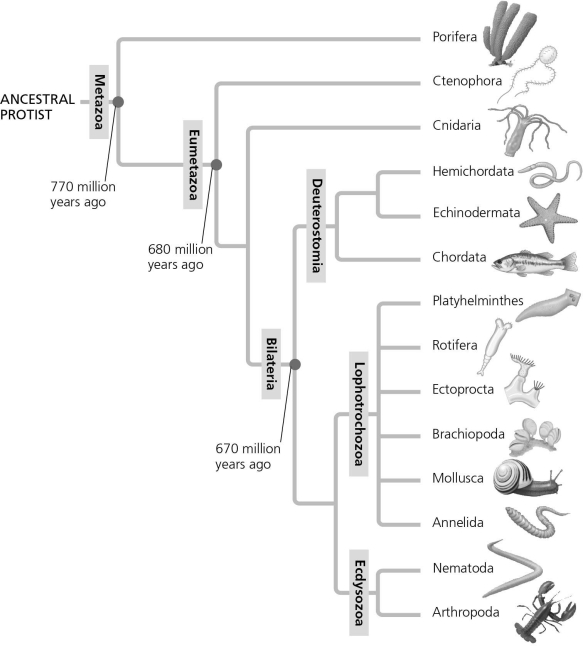
A) Ctenophora and Cnidaria
B) Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa
C) Cnidaria and Platyhelminthes
D) Echinodermata and Hemichordata
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using similarities in body symmetry and other anatomical features to assign an organism to a clade involves 1) cladistics based on body plan. 2) molecular-based phylogeny. 3) morphology-based phylogeny.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2 only
E) 1 and 3 only
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the current molecular evidence regarding animal origins is well substantiated in the future, then what will be true of any contrary evidence regarding the origin of animals derived from the fossil record?
A) The contrary fossil evidence will be seen as a hoax.
B) The fossil evidence will be understood to have been interpreted incorrectly because it is incomplete.
C) The fossil record will henceforth be ignored.
D) Phylogenies involving even the smallest bit of fossil evidence will need to be discarded.
E) Only phylogenies based solely on fossil evidence will need to be discarded.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The members of which clade in the phylum Cnidaria occur only as polyps?
A) Hydrozoa
B) Scyphozoa
C) Anthozoa
D) Arthropoda
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
Placozoan evolutionary relationships to other animals are currently unclear, and different phylogenies can be created, depending on the characters used to infer relatedness. Placozoans are multicellular invertebrates with a simple structure of only two tissue layers and only four cell types. They have the smallest amount of DNA measured in any animal. In comparison, sponges have no tissues but about 20 cell types. One species of placozoans, Tp (Trichoplax adhaerens) , produces a neuropeptide almost identical to one found in cnidarians. The genome of Tp, although the smallest of any known animal, shares many features of complex eumetazoan (even human!) genomes. The next three questions refer to the phylogenetic trees that follow. In the trees, the outgroup is a taxon that is outside the group of interest; members of the group of interest are more closely related to one another than to the outgroup. 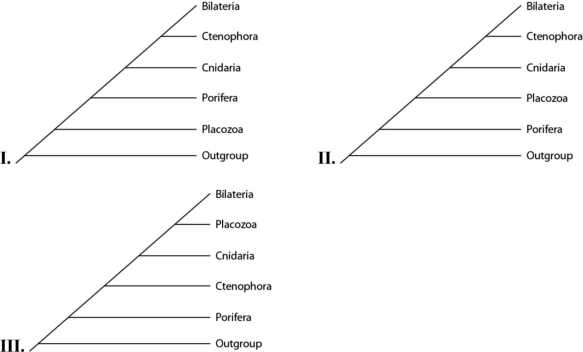 -Which tree(s) has (have) been created by emphasizing a protein found in placozoans?
-Which tree(s) has (have) been created by emphasizing a protein found in placozoans?
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Humans widely use pesticides on plants as a means to control insect and plant pests. However, pesticides are not selective in what they kill, so they often kill beneficial insect and plant species as well. This unintentional consequence favors plant and insect species that are pesticide resistant. This scenario is an example of
A) human impacts on evolution.
B) reciprocal selection.
C) human impacts on antibiotic resistance.
D) mass extinction of plant species.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which extant chordates are postulated to be most like the earliest chordates in physical appearance?
A) lancelets
B) adult tunicates
C) amphibians
D) reptiles
E) chondrichthyans
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange these taxonomic terms from most inclusive (most general) to least inclusive (most specific) . 1) lobe-fins 2) amphibians 3) gnathostomes 4) osteichthyans 5) tetrapods
A) 4, 3, 1, 5, 2
B) 4, 3, 2, 5, 1
C) 4, 2, 3, 5, 1
D) 3, 4, 1, 5, 2
E) 3, 4, 5, 1, 2
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 88
Related Exams