A) catabolism (catabolic pathways)
B) metabolism
C) anabolism (anabolic pathways)
D) dehydration
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A system at chemical equilibrium ________.
A) consumes energy at a steady rate
B) releases energy at a steady rate
C) consumes or releases energy, depending on whether it is exergonic or endergonic
D) has zero kinetic energy
E) can do no work
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Zinc, an essential trace element for most organisms, is present in the active site of the enzyme carboxypeptidase. The zinc most likely functions as ________.
A) a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme
B) a noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme
C) an allosteric activator of the enzyme
D) a cofactor necessary for enzyme activity
E) a coenzyme derived from a vitamin
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure. 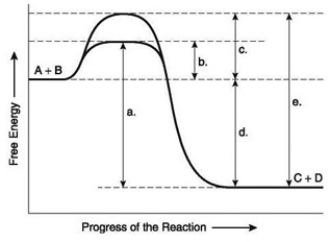 -Which of the following represents the activation energy required for a noncatalyzed reaction in the figure?
-Which of the following represents the activation energy required for a noncatalyzed reaction in the figure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure.  -Which of the following in the figure would be the same in either an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction?
-Which of the following in the figure would be the same in either an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Living organisms increase in complexity as they grow, resulting in a decrease in the entropy of an organism. How does this relate to the second law of thermodynamics?
A) Living organisms do not obey the second law of thermodynamics, which states that entropy must increase with time.
B) Life obeys the second law of thermodynamics because the decrease in entropy as the organism grows is exactly balanced by an increase in the entropy of the universe.
C) Living organisms do not follow the laws of thermodynamics.
D) As a consequence of growing, organisms cause a greater increase in entropy in their environment than the decrease in entropy associated with their growth.
E) Living organisms are able to transform energy into entropy.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When chemical, transport, or mechanical work is done by an organism, what happens to the heat generated?
A) It is used to power yet more cellular work.
B) It is used to store energy as more ATP.
C) It is used to generate ADP from nucleotide precursors.
D) It is lost to the environment.
E) It is transported to specific organs such as the brain.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solution of starch at room temperature does NOT readily decompose to form a solution of simple sugars because ________.
A) the starch solution has less free energy than the sugar solution
B) the hydrolysis of starch to sugar is endergonic
C) the activation energy barrier for this reaction cannot easily be surmounted at room temperature
D) starch cannot be hydrolyzed in the presence of so much water
E) starch hydrolysis is nonspontaneous
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some of the drugs used to treat HIV patients are competitive inhibitors of the HIV reverse transcriptase enzyme. Unfortunately, the high mutation rate of HIV means that the virus rapidly acquires mutations with amino acid changes that make them resistant to these competitive inhibitors. Where in the reverse transcriptase enzyme would such amino acid changes most likely occur in drug-resistant viruses?
A) in or near the active site
B) at an allosteric site
C) at a cofactor binding site
D) in regions of the protein that determine packaging into the virus capsid
E) Such mutations could occur anywhere with equal probability.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
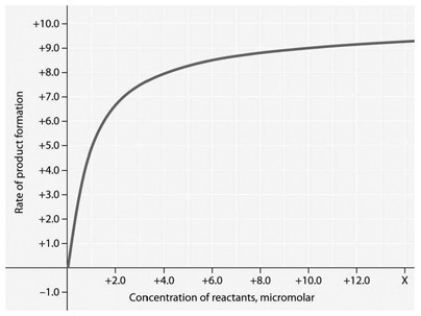 Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant
Concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant.
In the accompanying figure, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant
Concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant.
In the accompanying figure, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
A) Feedback inhibition by product occurs at high reactant concentrations.
B) Most enzyme molecules are occupied by substrate at high reactant concentrations.
C) The reaction nears equilibrium at high reactant concentrations.
D) The activation energy for the reaction increases with reactant concentration.
E) The rate of the reverse reaction increases with reactant concentration.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure.  -Which of the following represents the activation energy needed for the noncatalyzed reverse reaction, C + D → A + B, in the figure?
-Which of the following represents the activation energy needed for the noncatalyzed reverse reaction, C + D → A + B, in the figure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE about enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
A) The reaction is faster than the same reaction in the absence of the enzyme.
B) The free-energy change of the reaction is opposite from the reaction that occurs in the absence of the enzyme.
C) An enzyme catalyzes a reaction by raising the activation energy.
D) Enzyme-catalyzed reactions require energy to activate the enzyme.
E) Enzyme-catalyzed reactions release more free energy than noncatalyzed reactions.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below. A series of enzymes catalyze the reaction X → Y → Z → A. Product A binds to the enzyme that converts X to Y at a position remote from its active site. This binding decreases the activity of the enzyme. -What is substance X?
A) a coenzyme
B) an allosteric inhibitor
C) a substrate
D) an intermediate
E) the product
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is TRUE for all exergonic reactions?
A) The products have more total energy than the reactants.
B) The reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy.
C) The reaction goes only in a forward direction: All reactants will be converted to products, but no products will be converted to reactants.
D) A net input of energy from the surroundings is required for the reactions to proceed.
E) The reactions are rapid.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure.  -Which of the following represents the difference between the free-energy content of the reactants and the free-energy content of the products in the figure?
-Which of the following represents the difference between the free-energy content of the reactants and the free-energy content of the products in the figure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure.  -You have isolated a previously unstudied protein, identified its complete structure in detail, and determined that it catalyzes the breakdown of a large substrate. You notice it has two binding sites. One of these is large, apparently the bonding site for the large substrate; the other is small, possibly a binding site for a regulatory molecule. What do these findings tell you about the mechanism of this protein?
-You have isolated a previously unstudied protein, identified its complete structure in detail, and determined that it catalyzes the breakdown of a large substrate. You notice it has two binding sites. One of these is large, apparently the bonding site for the large substrate; the other is small, possibly a binding site for a regulatory molecule. What do these findings tell you about the mechanism of this protein?
A) It is probably a structural protein that is involved in cell-to-cell adhesion.
B) It is probably an enzyme that works through allosteric regulation.
C) It is probably an enzyme that works through competitive inhibition.
D) It is probably a cell membrane transport protein-like an ion channel.
E) It is probably a structural protein found in cartilage or skeletal tissue.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mathematical expression for the change in free energy of a system is ΔG =ΔH − TΔS. Which of the following is (are) correct?
A) ΔS is the change in enthalpy, a measure of randomness.
B) ΔH is the change in entropy, the energy available to do work.
C) ΔG is the change in free energy.
D) T is the temperature in degrees Celsius.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When 10,000 molecules of ATP are hydrolyzed to ADP and i in a test tube, about half as much heat is liberated as when a cell hydrolyzes the same amount of ATP. Which of the following is the best explanation for this observation?
A) Cells are open systems, but a test tube is an isolated system.
B) Cells are less efficient at heat production than nonliving systems.
C) The hydrolysis of ATP in a cell produces different chemical products than does the reaction in a test tube.
D) The reaction in cells must be catalyzed by enzymes, but the reaction in a test tube does not need enzymes.
E) Reactant and product concentrations in the test tube are different from those in the cell.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whenever energy is transformed, there is always an increase in the ________.
A) free energy of the system
B) free energy of the universe
C) entropy of the system
D) entropy of the universe
E) enthalpy of the universe
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An important group of peripheral membrane proteins are enzymes such as the phospholipases that cleave the head groups of phospholipids. What properties must these enzymes exhibit?
A) resistance to degradation
B) independence from cofactor interaction
C) water solubility
D) lipid solubility
E) membrane-spanning domains
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 60
Related Exams