A) The coordination number of atoms in hcp and fcc structures is 12.
B) The coordination number of atoms in simple cubic structures is 6.
C) The coordination number of atoms in bcc structures is 8.
D) A bcc structure has a higher packing efficiency than a simple cubic structure.
E) A bcc structure has a higher packing efficiency than a fcc structure.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lead crystallizes in the face-centered cubic lattice.What is the coordination number for Pb?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following phase diagram and identify the process occurring as one goes from point C to point D. 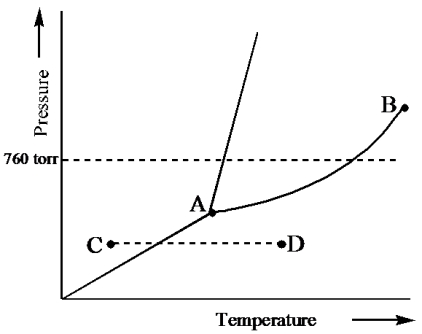
A) increasing temperature with a phase change from solid to liquid
B) increasing temperature with a phase change from solid to vapor
C) increasing temperature with a phase change from liquid to vapor
D) increasing temperature with no phase change
E) increasing temperature beyond the critical point
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Hexagonal close packing of identical atoms occurs when close-packed layers are stacked in an abcabc....arrangement.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In metals,the conduction bands and valence bands of the molecular orbitals are separated by a large energy gap.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following liquids is likely to have the highest surface tension?
A) Br2
B) C8H18
C) CH3OCH3
D) CH3OH
E) Pb
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following atoms should have the greatest polarizability?
A) F
B) Br
C) Po
D) Pb
E) He
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning a face-centered cubic unit cell and the corresponding lattice,made up of identical atoms,is incorrect?
A) The coordination number of the atoms in the lattice is 8.
B) The packing in this lattice is more efficient than for a body-centered cubic system.
C) If the atoms have radius r,then the length of the cube edge is r.
D) There are four atoms per unit cell in this type of packing.
E) The packing efficiency in this lattice and hexagonal close packing are the same.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The energy of a hydrogen bond is greater than that of a typical covalent bond.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following should have the highest boiling point?
A) CF4
B) CCl4
C) CBr4
D) CI4
E) CH4
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A metal such as chromium in the body-centered cubic lattice will have _______________ atom(s) per unit cell.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 9
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phase diagram for xenon has a solid-liquid curve with a positive slope.Which of the following is true?
A) Solid xenon has a higher density than liquid xenon.
B) Solid xenon has the same density as liquid xenon.
C) The phase diagram cannot be used to predict which phase of xenon is denser.
D) Freezing xenon is an endothermic process.
E) None of these statements is true.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the solid forms of the following elements,which one is most likely to be of the molecular type?
A) Xe
B) C
C) Pb
D) S
E) Cr
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Assuming that atoms are spherical,calculate the fraction of space which is occupied by atoms (i.e. ,the packing efficiency)in a metal with a simple cubic unit cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
The density of solid sodium chloride,NaCl,is 2.17 g/cm3.Use your knowledge of the sodium chloride lattice to calculate the spacing between Na+ and Cl- nearest neighbors,in cm.(Atomic masses (amu)are: Na,22.99;Cl,35.45.Also,1 amu = 1.661 10-24 g)
Correct Answer

verified
2.82 \(\times\) 10-8 cm
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comparing the energies of the following intermolecular forces on a kJ/mol basis,which would normally have the highest energy (i.e. ,be the strongest force) ?
A) ion-induced dipole
B) dipole-induced dipole
C) ion-dipole
D) dipole-dipole
E) dispersion
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the pair of substances in which the one with the higher vapor pressure at a given temperature is listed first.
A) C7H16,C5H12
B) CCl4,CBr4
C) H2O,H2S
D) CH3CH2OH,CH3-O-CH3
E) Xe,Kr
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neon condenses due to
A) dipole-dipole forces.
B) London dispersion forces.
C) hydrogen bonding.
D) covalent bonding.
E) intramolecular forces.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A temperature increase causes __________________ in the conductivity of a semiconductor.
A) a decrease
B) an increase
C) a modulation
D) an increase or decrease (depending on the semiconductor)
E) no change
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cubic unit cell has an edge length of 400.pm.The length of its body diagonal (internal diagonal) in pm is therefore
A) 512
B) 566
C) 631
D) 693
E) 724
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 89
Related Exams