A) $14
B) −$8
C) $0
D) $46.62
E) $54
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts a monopoly market in the absence of price discrimination. Consumer surplus in this market is represented by the area:
Figure 9.8
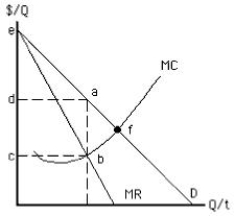
A) eda.
B) ecf.
C) dacb.
D) dafc.
E) abf.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows a non-discriminating monopolist. The total revenue earned by the monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is _____.
Figure 9.1
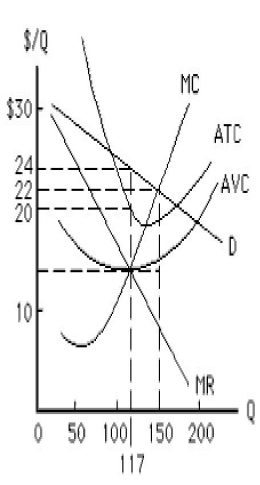
A) $2,574
B) $2,808
C) $2,100
D) $1,638
E) $3,300
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a monopolist. Assume that the marginal cost of production is equal to the average total cost at the profit maximizing output level. The maximum profit for this monopolist if he does not practice price discrimination is _____.
Figure 9.4
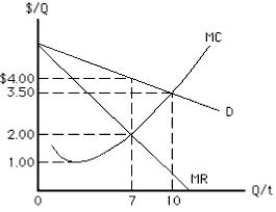
A) $4
B) $14
C) $3.50
D) $21
E) $4.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes a monopolized market structure?
A) A market structure with a single buyer
B) Many firms with no control over price producing identical products with no differentiation
C) A few firms with some control over price producing similar products which are close substitutes
D) A few firms with no control over price producing highly differentiated products
E) A single firm producing a highly differentiated product and serving the entire market
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true for a monopolist?
A) Marginal revenue is maximized where demand is unit elastic.
B) Total revenue is maximized where demand is inelastic.
C) Marginal revenue is negative where demand is inelastic.
D) Total revenue is negative where demand is elastic.
E) Marginal revenue is lowest where demand is unit elastic.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the total cost and total revenue curves for a monopolist. The profit-maximizing price charged by the monopolist is:
Figure 9.3
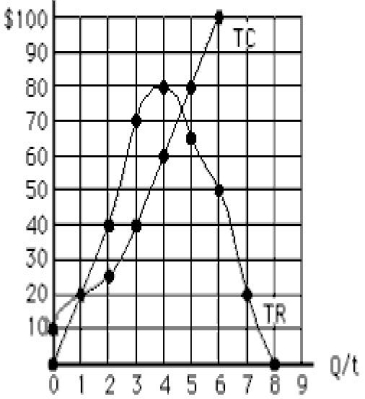
A) $70.
B) $80.
C) $23.33.
D) $20.
E) $40.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Anything that prevents new firms from competing on an equal basis with existing firms in an industry is called a barrier to entry.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely to be true of a monopoly in long-run equilibrium if it enjoys a patent and earns economic profit in the short run?
A) It will earn only a normal profit in the long run.
B) It will suffer an economic loss and stop producing in the long run.
C) It will earn a positive economic profit in the long run.
D) It will achieve productive efficiency in the long run.
E) It will achieve allocative efficiency in the long run.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Total deadweight loss in society is reduced through rent seeking by monopolists.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is likely to be true of perfect competition but not of monopoly?
A) A firm can produce a good only if government licenses authorize it to produce the good.
B) A firm can sell a good in the market only if the government grants a patent to the firm.
C) A firm can earn economic profit in the long run.
D) A firm can shut down in the short run only if the price charged by it exceeds the average variable cost of production.
E) A firm can face competition from new entrants into the market in the long run.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a monopolist. The maximum profit earned by the non-discriminating monopolist is:
Figure 9.6
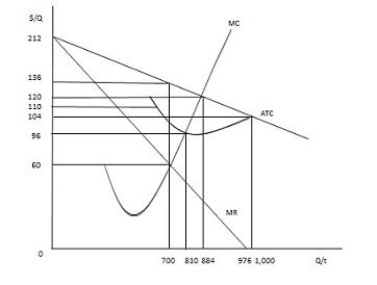
A) $95,200.
B) $84,000.
C) $53,200.
D) $42,000.
E) $18,200.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist that engages in perfect price discrimination:
A) divides all buyers into two mutually exclusive groups.
B) refuses to sell its output to consumers of rival brands.
C) charges the same price for every unit sold.
D) charges a different price for every unit sold.
E) charges a high price to bulk consumers of its product.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a single firm supplies all the ceramic windlasses in the U.S. The demand curve that the firm faces is:
A) elastic everywhere.
B) unit elastic everywhere.
C) inelastic only at the profit-maximizing output.
D) perfectly inelastic everywhere.
E) elastic only at the profit-maximizing output.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Perfectly competitive firms and monopolistic firms determine their respective profit-maximizing output levels where:
A) price equals marginal cost.
B) total revenue is maximized.
C) average total cost is minimized.
D) marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
E) price is at the maximum possible level.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist producing a level of output at which market demand is inelastic, _____.
A) short-run profit is maximum.
B) a decrease in price increases total revenue.
C) a decrease in price decreases total cost.
D) a decrease in price decreases total revenue.
E) an increase in output increases short-run economic profit.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Barriers to entry:
A) cause monopolies to experience diseconomies of scale in the long run.
B) prevent monopolies from earning profit in the short run.
C) may allow monopolies to earn profit in the long run.
D) prevent government from regulating a monopoly.
E) prevent a natural monopoly from raising its price.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a non-discriminating monopolist. The total cost incurred by the monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is _____.
Figure 9.1
A) $3,300
B) $3,400
C) $2,808
D) $2,340
E) $1,638
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopolist that does not practice price discrimination is operating at an output level where price equals average total cost, we can conclude that:
A) its economic profit is $0.
B) it is not maximizing profit.
C) it should go out of business in the long run.
D) it is not earning a normal profit.
E) it should shut down in the short run.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major fruit juice manufacturer fails in its attempt to engage in price discrimination between students and all other consumers of fruit juice. Which of the following explanations is most likely to account for this failure?
A) The students resold the juice to other consumers.
B) The market for fruit juice was monopolistically competitive.
C) The price elasticity of demand for fruit juice was different for each group.
D) The cost of producing the fruit juice was extremely high.
E) The students preferred to purchase juice from other small juice manufacturers.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 150
Related Exams