B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Ratios are used only by company management, and not investors, to evaluate the financial health of a company.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The percent-of-sales method of computing uncollectible accounts is used for:
A) interim statements because it is more accurate than the aging method.
B) annual statements because it is more accurate than the aging method.
C) interim statements because it is easier than the aging method.
D) annual statements because it is easier than the aging method.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It takes good judgment, which includes ethics, to become a successful accountant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The creditor has a note payable.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
On March 1, 2011, Anya's Toy Store purchased Hasbro stock for $33,400 with the intent of selling the stock at a profit within a few months. On April 10, dividends of $1,075 were received from the Hasbro stock. On December 31, 2011, the end of Anya's Toy Store's calendar year, the Hasbro stock had a market value of $32,300. On January 3, 2012, Anya's Toy Store sold all of the Hasbro stock for $34,000. Prepare the journal entries needed to record the transactions for 2011 and 2012.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To record estimated bad debts under the direct write-off method:
A) debit Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts and credit Accounts Receivable.
B) debit Accounts Receivable and credit Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts.
C) debit Uncollectible-Accounts Expense and credit Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts.
D) no journal entry is needed.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When evaluating the collectability of accounts receivable:
A) the uncollectible-account expense is a contra account.
B) the allowance for uncollectible accounts is an operating expense in the selling, general and administrative category.
C) the allowance method uses estimates developed from the company's collection experience.
D) the direct write-off method uses the allowance for uncollectible accounts to record bad debts.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which method does NOT use estimates?
A) Direct-write off method
B) Percent-of-Sales
C) Aging-of-receivables method
D) Allowance method
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The maturity value of a $40,000 note at 11% for 5 months is (round to nearest dollar) :
A) $41,833.
B) $40,880.
C) $44,400.
D) $47,260.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Short-term investments:
A) are reported after accounts receivable on the balance sheet.
B) are more liquid than cash.
C) are reported at historical cost on the balance sheet.
D) include trading securities.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under the allowance method:
A) the company records the uncollectible-account expense when the customer does not pay.
B) the allowance for uncollectible accounts is a contra account to gross revenue.
C) the allowance for uncollectible accounts will normally have a debit balance.
D) the company sets up an allowance for uncollectible accounts to estimate the amount of the receivables the company does not expect to collect.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
XYZ Company has decided to factor its accounts receivable in order to get the immediate receipt of cash. The journal entry to record the factoring of the receivables would include:
A) a debit to Accounts Receivable.
B) a credit to Cash.
C) a debit to Financing Expense.
D) a credit to Interest Revenue.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following item appeared on a balance sheet: Receivables, less allowance of $100,855 …..$1,432,602 The gross balance in Accounts Receivable before the allowance was deducted was:
A) $1,331,747.
B) $1,432,602.
C) $1,533,457.
D) cannot be determined from the facts.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The journal entry to record uncollectible-account expense includes a credit to Accounts Receivable.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under the allowance method, the entry to write off a $2,600 uncollectible account includes a:
A) debit to Accounts Receivable for $2,600.
B) credit to Uncollectible-Account Expense for $2,600.
C) credit to Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts for $2,600.
D) debit to Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts for $2,600.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Complete the following chart by filling in the missing items. Use a 360-day year and round all answers to the nearest dollar and to 2 decimal places for percentages.
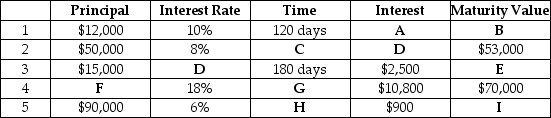
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
The Shady Bank lent Dorst Company $8,000 on December 1 for 6 months at an interest rate of 8%. The Shady Bank has a year end of December 31. Prepare the journal entries to record the (1) issuance of the note, (2) the accrued interest at December 31, and (3) the collection of the note on June 1. Round any amounts to the nearest dollar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All investments in marketable securities NOT classified as trading securities or held-to-maturity securities are classified as:
A) debt securities.
B) equity securities.
C) marketable securities.
D) available-for-sale securities.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The direct write-off method records uncollectible-account expense:
A) at the end of the year.
B) at the end of the accounting period.
C) when the specific account receivable is determined to be uncollectible.
D) under the percent-of-sale method.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 201
Related Exams