A) 36%
B) 32%
C) 28%
D) 24%
E) 20%
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major disadvantage of the payback period method is that it
A) Is useless as a risk indicator.
B) Ignores cash flows beyond the payback period.
C) Does not directly account for the time value of money.
D) All of the above are correct.
E) Only answers b and c are correct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Under certain conditions, a particular project may have more than one IRR.One condition under which this situation can occur is if, in addition to the initial investment at time = 0, a negative cash flow occurs at the end of the project's life.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
New Project NPV Truck Acquisition You have been asked by the president of your company to evaluate the proposed acquisition of a new special-purpose truck.The truck's basic price is $50,000, and it will cost another $10,000 to modify it for special use by your firm.The truck falls into the MACRS three-year class, and it will be sold after three years for $20,000.Use of the truck will require an increase in net working capital (spare parts inventory) of $2,000.The truck will have no effect on revenues, but it is expected to save the firm $20,000 per year in before-tax operating costs, mainly labor.The firm's marginal tax rate is 40 percent. [MACRS table required] -Refer to Truck Acquisition.What is the terminal (nonoperating) cash flow at the end of Year 3?
A) $10,000
B) $12,000
C) $15,680
D) $16,000
E) $18,000
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If an asset being considered for acquisition has beta of zero, its purchase will have no effect on the firm's market risk.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The change in net working capital that results from the acceptance of a project is an incremental cash flow that must be considered in capital budgeting analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following information, what is the required cash outflow associated with the acquisition of a new machine; that is, in a project analysis, what is the initial investment outlay at t = 0? 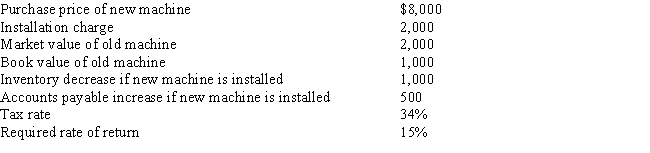
A) −$8,980
B) −$6,460
C) −$5,200
D) −$6,840
E) −$12,020
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company is analyzing two mutually exclusive projects, S and L, whose cash flows are shown below:  The company's required rate of return is 12 percent, and it can get an unlimited amount of funds at that rate.What is the IRR of the better project, i.e., the project which the company should choose if it wants to maximize the price of its stock?
The company's required rate of return is 12 percent, and it can get an unlimited amount of funds at that rate.What is the IRR of the better project, i.e., the project which the company should choose if it wants to maximize the price of its stock?
A) 12.00%
B) 15.53%
C) 18.62%
D) 19.08%
E) 20.46%
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Target Copy Company is contemplating the replacement of its old printing machine with a new model costing $60,000.The old machine, which originally cost $40,000, has 6 years of expected life remaining and a current book value of $30,000 versus a current market value of $24,000.Target's corporate tax rate is 40 percent.If Target sells the old machine at market value, what is the initial investment outlay (after-tax) for the new printing machine?
A) −$22,180
B) −$30,000
C) −$33,600
D) −$36,000
E) −$40,000
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Conflicts between two mutually exclusive projects, where the NPV method chooses one project but the IRR method chooses the other, should generally be resolved in favor of the project with the higher NPV.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The NPV will be positive if the IRR is less than the required rate of return.
B) If the multiple IRR problem does not exist, any independent project acceptable by the NPV method will also be acceptable by the IRR method.
C) When IRR = r (the required rate of return) , NPV = 0.
D) The IRR can be positive even if the NPV is negative.
E) The NPV method is not affected by the multiple IRR problem.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Klott Company encounters significant uncertainty with its sales volume and price in its primary product.The firm uses scenario analysis in order to determine an expected NPV, which it then uses in its budget.The base case, best case, and worse case scenarios and probabilities are provided in the table below.What is Klott's expected NPV, standard deviation of NPV, and coefficient of variation of NPV? 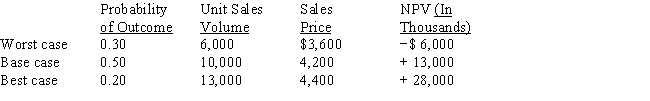
A) Expected NPV = $35,000; σNPV = 17,500; CVNPV = 2.0.
B) Expected NPV = $35,000; σNPV = 11,667; CVNPV = 0.33.
C) Expected NPV = $10,300; σNPV = 12,083; CVNPV = 1.17.
D) Expected NPV = $13,900; σNPV = 8,476; CVNPV = 0.61.
E) Expected NPV = $10,300; σNPV = 13,900; CVNPV = 1.35.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your company is considering a machine that will cost $1,000 at Time 0 and which can be sold after 3 years for $100.To operate the machine, $200 must be invested at Time 0 in inventories; these funds will be recovered when the machine is retired at the end of Year 3.The machine will produce sales revenues of $900/year for 3 years; variable operating costs (excluding depreciation) will be 50 percent of sales.Operating cash inflows will begin 1 year from today (at Time 1) .The machine will have depreciation expenses of $500, $300, and $200 in Years 1, 2, and 3, respectively.The company has a 40 percent tax rate, enough taxable income from other assets to enable it to get a tax refund from this project if the project's income is negative, and a 10 percent required rate of return.Inflation is zero.What is the project's NPV?
A) $6.24
B) $7.89
C) $8.87
D) $9.15
E) $10.41
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the calculated NPV is negative, then which of the following must be true? The discount rate used is
A) Equal to the internal rate of return.
B) Too high.
C) Greater than the internal rate of return.
D) Too low.
E) Less than the internal rate of return.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Normal Projects Q and R have the same NPV when the discount rate is zero.However, Project Q has larger early cash flows than R.Therefore, we know that at all discount rates greater than zero, Project R will have a greater NPV than Q.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Small businesses probably make less use of the DCF capital budgeting techniques than large businesses.This may reflect a lack of knowledge on the part of small firms' managers, but it may also reflect a rational conclusion that the costs of using DCF analysis outweigh the benefits of these methods for those firms.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Virus Stopper Inc., a supplier of computer safeguard systems, uses a required rate of return of 12 percent to evaluate average risk projects, and it adds or subtracts 2 percentage points to evaluate projects of more or less risk.Currently, two mutually exclusive projects are under consideration.Both have a cost of $200,000 and will last 4 years.Project A, a riskier-than-average project, will produce annual end of year cash flows of $71,104.Project B, of less than average risk, will produce cash flows of $146,411 at the end of Years 3 and 4 only.Virus Stopper should accept
A) B with a NPV of $10,001.
B) Both A and B because both have NPVs greater than zero.
C) B with a NPV of $8,042.
D) A with a NPV of $7,177.
E) A with a NPV of $15,968.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Risk-Adjusted Discount Rate Real Time Inc. The president of Real Time Inc.has asked you to evaluate the proposed acquisition of a new computer.The computer's price is $40,000, and it falls into the MACRS 3-year class.Purchase of the computer would require an increase in net working capital of $2,000.The computer would increase the firm's before-tax revenues by $20,000 per year but would also increase operating costs by $5,000 per year.The computer is expected to be used for 3 years and then be sold for $25,000.The firm's marginal tax rate is 40 percent, and the project's required rate of return is 14 percent. [MACRS table required] -Refer to Real Time Inc.What is the project's NPV?
A) $2,622
B) $2,803
C) $2,917
D) $5,712
E) $6,438
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When evaluating a new project, the firm should consider all of the following factors except:
A) Changes in working capital attributable to the project.
B) Previous expenditures associated with a market test to determine the feasibility of the project, if the expenditures have been expensed for tax purposes.
C) The current market value of any equipment to be replaced.
D) The resulting difference in depreciation expense if the project involves replacement.
E) All of the above should be considered.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) In a capital budgeting analysis where part of the funds used to finance the project are raised as debt, failure to include interest expense as a cost when determining the project's supplemental operating cash flows will lead to an upward bias in the NPV.
B) The preceding statement would be true if "upward" were replaced with "downward."
C) The existence of "externalities" reduces the NPV to a level below the value that would exist in the absence of externalities.
D) If one of the assets that would be used by a potential project is already owned by the firm, and if that asset could be leased to another firm if the project is not undertaken, then the net rent that could be obtained should be charged as a cost (initial investment outlay) to the project under consideration.
E) The rent referred to in statement d is a sunk cost, and as such it should be ignored.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 201
Related Exams