A) H2O
B) MgCl2
C) NaNO3
D) KOH
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the reaction shown is correctly balanced,the coefficients are: KClO3 → KCl + O2
A) 1,1,1
B) 2,2,2
C) 2,2,3
D) 2,2,1
E) 4,4,6
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a chemical reaction
A) there are equal numbers of atoms on each side of the reaction arrow.
B) there are equal numbers of molecules on each side of the reaction arrow.
C) there are always the same number of products as there are reactants.
D) the number of atoms present in a reaction can vary when the conditions change during the reaction.
E) none of the above
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the following reaction which species is being oxidized and which is being reduced? 2 Cr (s) + 3 Cl2 (g) → 2 CrCl3 (s)
A) oxidized: Cr; reduced: CrCl3
B) oxidized:CrCl3; reduced: Cr
C) oxidized: Cr; reduced: Cl2
D) oxidized: Cl2; reduced: Cr
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reduction is the process of
A) gaining hydrogen.
B) losing oxygen.
C) gaining electrons.
D) forming an anion from a neutral atom.
E) all of the above
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the reaction shown is correctly balanced,the coefficients are: ____ HBr + ____ Ca(OH) 2 → ____ CaBr2 + ____ H2O
A) 2,1,1,1
B) 1,1,1,2
C) 2,1,1,2
D) 2,2,1,1
E) 2,1,2,2
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the reaction shown is correctly balanced,the coefficients are: C6H14 (l) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + H2O (g)
A) 1,6,6,7
B) 2,19,12,14
C) 1,3.5,6,7
D) 1,9.5,6,7
E) 2,16.5,12,7
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the reaction shown and identify the statement that is not true.
CaCO3 (s) 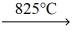 CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
A) This reaction is balanced as written.
B) The reactant must be heated for this reaction to occur.
C) The products are a solid and a gas.
D) Water must be present for this reaction to occur.
E) There are no solutions used in this reaction.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -LX (aq) + MY (aq) → LY (s) + MX (aq)
A) redox
B) acid-base
C) precipitation
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the spectator ions in the reaction between KOH and HNO3?
A) K+ and H+
B) H+ and OH-
C) K+ and NO3-
D) H+and NO3-
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The combination of ions least likely to produce a precipitate is
A) Ba2+ and SO42-.
B) Pb+ and Cl-.
C) Ca2+ and PO43-.
D) Fe3+ and OH-.
E) Mg2+ and C2H3O2-.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
2 AgNO3 (aq) + K2SO4(aq) → 2 KNO3 (aq) + Ag2SO4s) The net ionic reaction for the balanced equation shown above is
A) Ag+ +![]()
→ AgNO3.
B) 2 K+ +![]()
→ K2SO4.
C) K+ +![]()
→ KNO3.
D) 2 Ag+ +![]()
→ Ag2SO4.
E) H+ + OH- → H2O.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following reaction can be classified as what type(s) of reaction(s) ? 2 Al(OH) 3 (aq) + 3 H2SO4 (aq) → Al2(SO4) 3 (s) + 6 H2O (l)
A) precipitation
B) acid-base neutralization
C) redox reaction
D) both A and B
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is always a spectator ion in a chemical reaction?
A) Na+
B) Cl-
C) S2-
D) Mg2+
E) All of these ions.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following. -HR (aq) + XOH (aq) → XR (aq) + H2O (l)
A) redox
B) acid-base
C) precipitation
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reaction is not an example of a redox reaction?
A) 2 Hg (l) + O2 (g) → 2 HgO (s)
B) 2 (NH4) 3PO4 (aq) + 3 Ba(NO3) 2 (aq) → Ba3(PO4) 2 (s) + 6 NH4NO3 (aq)
C) CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)
D) 6 HCl (aq) + 2 Al (s) → 2 AlCl3 (aq) + 3 H2 (g)
E) 2 Al2O3 (s) → 4 Al (s) + 3 O2 (g)
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The scientific principle which is the basis for balancing chemical equations is
A) the Law of Conservation of Energy.
B) the Law of Conservation of Mass.
C) the Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
D) the Law of Definite Proportions.
E) Avogadro's Law.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the statements regarding redox reactions are true except
A) a reducing agent causes another substance to be reduced.
B) halogens usually behave as oxidizing agents because they readily gain electrons.
C) metal ions are produced when pure metals are oxidized.
D) when a substance is oxidized its charge (or oxidation number) decreases.
E) alkali metals often behave as reducing agents because they readily lose electrons.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following equations is not balanced?
A) C7H16 + O2 → 7 CO2 + 8 H2O
B) K2CrO4 + Pb(NO3) 2 → 2 KNO3 + PbCrO4
C) 4 Fe3O4 + O2 → 6 Fe2O3
D) 3 AgNO3 + (NH4) 3PO4 → Ag3PO4 + 3 NH4NO3
E) 2 Al2O3 → 4 Al + 3 O2
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The combination of ions most likely to produce a precipitate is
A) Li+ and PO43-.
B) Pb2+ and NO3-.
C) NH4+ and SO42-.
D) Fe3+ and OH-.
E) Mg2+ and C2H3O2-.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 53
Related Exams