A) glucose,water
B) oxygen,glucose
C) oxygen,water
D) glucose,carbon dioxide
E) glucose,oxygen
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cyanide is a poison that binds to the final carrier in the electron transport chain.Why does this property make cyanide deadly?
A) Cyanide prevents the reduction of oxygen and stops the electron transport chain.
B) Cyanide inhibits the reduction of NAD+ and FAD.
C) Cyanide blocks the channel through the ATP synthase complex.
D) Cyanide causes ATP hydrolysis.
E) Cyanide inhibits the formation of lactate from pyruvatE.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the reactants involved in cellular respiration?
A) glucose and water
B) carbon dioxide and water
C) oxygen and glucose
D) carbon dioxide and glucose
E) water and oxygen
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the net yield of ATP from glycolysis of one glucose molecule?
A) 0 ATP
B) 4 ATP
C) 2 ATP
D) 6 ATP
E) 10 ATP
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the benefit of converting pyruvate to lactate when oxygen is not available?
A) It allows the electron transport chain to continue.
B) It allows chemiosmosis to continue.
C) It allows the electron transport chain to produce oxygen.
D) It allows substrate-level ATP synthesis to continue.
E) It allows the Krebs cycle to produce oxygen.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molecule NAD+ is said to have an oxidative role in glycolysis because it accepts
A) phosphate atoms.
B) oxygen atoms.
C) carbon dioxide molecules.
D) electrons and hydrogen ions.
E) pyruvate molecules.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a baker wants to make bread,which of the following organisms must be used to make the dough rise?
A) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
B) Lactobacillus
C) Acetobacter aceti
D) Streptococcus thermophilus
E) Aspergillus
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In animals,under anaerobic conditions,pyruvate is converted to which of the following molecules?
A) glucose
B) lactate
C) NAD+
D) ATP
E) alcohol
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: 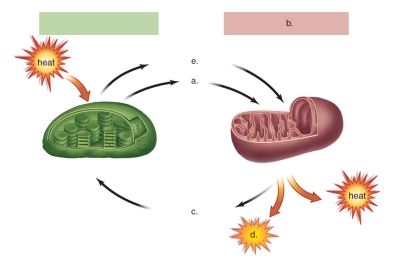 -This figure shows the relationship between the chloroplast and the mitochondrion.What does "b" represent?
-This figure shows the relationship between the chloroplast and the mitochondrion.What does "b" represent?
A) photosynthesis
B) Calvin cycle
C) glycolysis
D) cellular respiration
E) carbon fixation
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a product of a part of metabolism other than the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
A) NAD+
B) oxygen
C) ATP
D) FAD
E) water
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Degradative reactions which break down molecules are referred to as
A) deamination.
B) anabolism.
C) catabolism.
D) fermentation.
E) cellular respiration.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 51 of 51
Related Exams