A) Two genetically distinct types of haploid gametes
B) Two genetically distinct types of diploid gametes
C) Four genetically distinct types of haploid gametes
D) Four genetically distinct types of diploid gametes
E) Four genetically identical diploid gametes
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Homologous chromosomes contain the same ____ but may contain different ____.
A) Alleles, genes
B) Sister chromatids, genes
C) Alleles, sister chromatids
D) Genes, sister chromatids
E) Genes, alleles
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are tetraploid offspring considered a separate species from their diploid parents?
A) Their offspring would be diploid and sterile
B) Their offspring would be triploid and sterile
C) Their offspring would be tetraploid and sterile
D) The two species would look different and would not be pollinated
E) The two species would be in different habitats and not able to mate
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If daughter cells produced by meiosis have a mixture of paternal and maternal chromosomes this is due to:
A) Crossing over
B) Semi-conservative replication
C) Random fertilization
D) Random alignment of chromosome pairs
E) Mutation
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A species has 6 chromosomes in each diploid cell.How many genetically unique offspring could be produced from sexual reproduction in this species?
A) 64
B) 36
C) 16
D) 9
E) 8
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A diploid cell with 6 chromosomes would produce which of the following after meiosis?
A) Four genetically distinct types of haploid gametes
B) Two genetically distinct types of diploid gametes
C) Four genetically distinct types of diploid gametes
D) Eight genetically distinct types of haploid gametes
E) Eight genetically identical haploid gametes
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans,the egg provides the mitochondria to the zygote.In plants which organelles would be provided by the egg and not by the sperm?
A) Mitochondria
B) Chloroplasts
C) Nuclei
D) Chloroplasts and mitochondria
E) Nuclei and chloroplasts
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a haploid cell goes through meiosis it will generate:
A) Four haploid cells
B) This isn't possible
C) Two haploid cells
D) Four diploid cells
E) Two diploid cells
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diploid means having:
A) One complete set of chromosomes
B) Three complete sets of chromosomes
C) Two complete sets of chromosomes
D) Two chromosomes in each somatic cell
E) Two chromosomes in each gamete
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mitotic cell division creates identical copies by replicating a cell's DNA __________ and then dividing ____________.
A) Once, twice
B) Twice, once
C) Twice, twice
D) Once, once
E) None are correct
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process that merges the gametes from two parents is:
A) Fertilization
B) Meiosis
C) Parthenogenesis
D) Mitosis
E) Conjugation
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a woman in her late forties wants to have a baby and seeks medical advice,she would most likely be advised that she is at much greater risk of having a baby with Down syndrome.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9.19 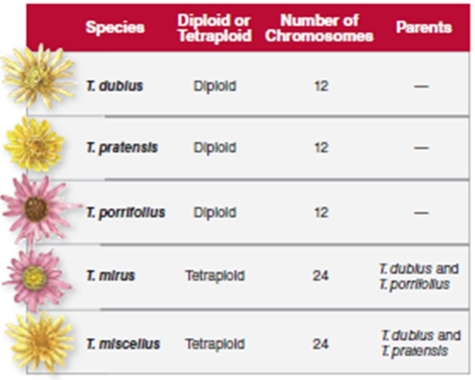 -Tragopogon mirus is a hybrid of T.dubius and T porrifolius.Based on Figure 9.19,T.mirus has:
-Tragopogon mirus is a hybrid of T.dubius and T porrifolius.Based on Figure 9.19,T.mirus has:
A) 12 chromosomes from T. d ubius and 12 chromosomes from T porrifolius
B) 6 chromosomes from T. dubius and 6 chromosomes from T porrifolius
C) 24 chromosomes from T. dubius and 24 chromosomes from T porrifolius
D) 24 chromosomes from T. dubius
E) 24 chromosomes from T porrifolius
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is it essential that meiosis produce haploid cells?
A) So that the number of chromosomes will double each generation
B) To produce haploid offspring
C) To prevent the number of chromosomes from doubling each generation
D) To produce diploid gametes
E) To allow asexual reproduction
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In plants,sporophytes undergo meiosis to produce ____ spores.
A) Diploid
B) Tetraploid
C) Triploid
D) Fertilized
E) Haploid
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mitosis occurs in germ cells throughout life.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans during meiosis,a diploid germ cell reduces its chromosome number by half to generate __________ haploid nuclei.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 23
E) 46
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most cultivated bananas are triploid.How could these be generated from diploid parent banana plants?
A) Non-disjunction in meiosis followed by normal fertilization
B) Non-disjunction in mitosis followed by normal fertilization
C) Fertilization of a haploid egg by two haploid sperm
D) Fertilization of a haploid egg by a haploid sperm
E) Fertilization of a diploid somatic cell by a haploid sperm
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a diploid sperm fertilizes a diploid egg it will produce a ____ zygote.
A) Triploid
B) Tetraploid
C) Diploid
D) Haploid
E) Hexaploid
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Human cell's have:
A) 23 pairs of chromosomes
B) 22 pairs of chromosomes
C) 44 chromosomes
D) 2 pairs of sex chromosomes
E) One pair of autosomes
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 81
Related Exams