A) a positive externality exists.
B) the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximised.
C) the market achieves economic efficiency.
D) a negative externality exists.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes how a negative externality affects a competitive market?
A) The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the social cost.
B) The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the private benefit from consumption.
C) The externality causes consumer surplus to exceed producer surplus.
D) The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the equilibrium price.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15.2 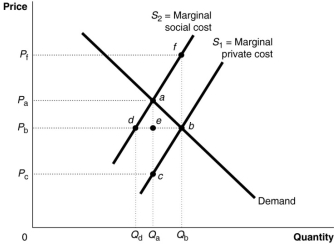 Figure 15.2 shows a market with a negative externality.
-Refer to Figure 15.2.What price represents the true marginal cost of the last unit produced?
Figure 15.2 shows a market with a negative externality.
-Refer to Figure 15.2.What price represents the true marginal cost of the last unit produced?
A) Pa
B) Pb
C) Pc
D) Pf.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a tax equal to the value of the marginal external cost at the optimal output is imposed on a pollution-generating good.All of the following will result from the tax except
A) an increase in the equilibrium market price.
B) a decrease in the equilibrium quantity produced and consumed.
C) a decrease in market supply of the good.
D) an increase in the demand for the good.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15.5 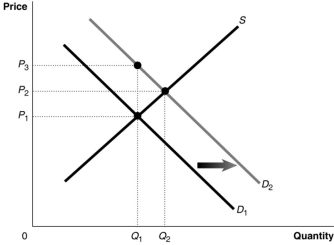 Figure 15.5 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
-Refer to Figure 15.5.If, because of an externality, the economically efficient output is Q2 and not the current equilibrium output of Q1, what does D1 represent?
Figure 15.5 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
-Refer to Figure 15.5.If, because of an externality, the economically efficient output is Q2 and not the current equilibrium output of Q1, what does D1 represent?
A) The demand curve reflecting external benefits
B) The demand curve reflecting social benefits
C) The demand curve reflecting private benefits
D) The demand curve reflecting the sum of private and social benefits
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15.4 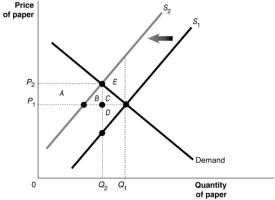 Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills, located upstream from a fishing village, discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river, and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 15.4 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Figure 15.4.Why is there a deadweight loss?
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills, located upstream from a fishing village, discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river, and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 15.4 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Figure 15.4.Why is there a deadweight loss?
A) Because the marginal social cost of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the marginal benefit
B) Because the marginal private cost of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the marginal benefit
C) Because the marginal social benefit of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the private cost
D) Because the marginal private benefit of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the social cost
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why will for-profit producers not produce public goods?
A) Markets exist for private goods but not for public goods.
B) The cost of production can be easily determined.
C) Buyers will not be willing to pay for the goods since the benefits are not excludable.
D) All external benefits can be internalised using market prices.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a command and control approach to reducing pollution?
A) The government sets a target for maximum emissions
B) The government imposed a per unit tax on the good that creates pollution
C) The government gives firms a tax rebate for every unit of pollution abated
D) None of the above
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Medical research that ends in a cure for a serious disease produces positive externalities.What is the impact of this positive externality on economic efficiency?
A) At equilibrium, less than the economically efficient quantity of medical research is produced.
B) A deadweight loss occurs because at equilibrium, the marginal social cost of medical research is greater than the marginal social benefit.
C) At equilibrium, more than the economically efficient quantity of medical research is produced.
D) A deadweight loss occurs because at equilibrium, the marginal social cost equals the marginal social benefit.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When the government imposes a tax equal to the external cost of producing a product that causes pollution, the government is said to externalise the externality.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15.14 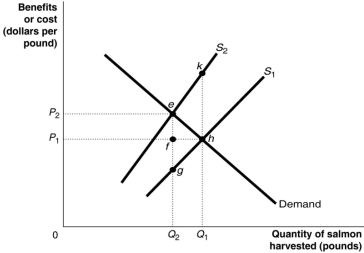 Figure 15.14 shows the market for Atlantic tuna, a common resource.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
-Refer to Figure 15.14.The current market equilibrium output is partly the result of overfishing.In that case, what does S1 represent?
Figure 15.14 shows the market for Atlantic tuna, a common resource.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
-Refer to Figure 15.14.The current market equilibrium output is partly the result of overfishing.In that case, what does S1 represent?
A) The private marginal cost of harvesting tuna
B) The social marginal cost of harvesting tuna
C) The private marginal benefit of harvesting tuna
D) The social marginal benefit of harvesting tuna
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An externality is an example of a market failure.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15.6 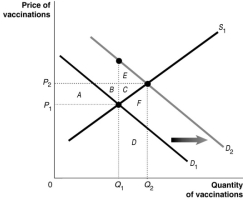 Figure 15.6 shows the market for measles vaccinations, a product whose use generates positive externalities.
-Refer to Figure 15.6.What does D1 represent?
Figure 15.6 shows the market for measles vaccinations, a product whose use generates positive externalities.
-Refer to Figure 15.6.What does D1 represent?
A) The demand curve reflecting social benefit
B) The positive externalities curve
C) The demand curve reflecting private benefit
D) The social welfare curve
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that production from an electric utility caused acid rain.If the government imposed a tax on the utility equal to the cost of the acid rain, the government's action would
A) externalise the externality.
B) result in a marginal social benefit greater than the marginal cost of the electricity.
C) be an example of supply side economic policy.
D) internalise the externality.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does the phrase 'internalising an external cost' mean?
A) Limiting the extent to which domestic firms can outsource production
B) Prohibiting economic activities that create externalities
C) Forcing producers to factor into their production costs the cost of the externalities created in the production of their output
D) Finding a way to address cross-border pollution
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One difference between the demand for a private good and that for a public good is that
A) with a private good, each consumer chooses the quantity she wants to consume but with a public good, each consumer chooses the price she is willing to pay for a fixed quantity.
B) with a private good, each consumer chooses the quantity she wants to consume but with a public good, everyone consumes the same quantity.
C) with a private good, each consumer receives different amounts of benefit from consuming the product but with a public good, every consumer realises the same amount of benefit from consuming the product.
D) the marginal benefit from consuming the last unit of a public good always exceeds the marginal benefit from consuming the last unit of a private good because there are externalities in the consumption of the former.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A market failure arises when an entire sector of the economy (for example, the airline industry)collapses because of some unforeseen event.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When there is a negative externality, the private cost of production ________ the social cost of production.
A) is greater than
B) is equal to
C) eliminates
D) is less than
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15.6  Figure 15.6 shows the market for measles vaccinations, a product whose use generates positive externalities.
-Refer to Figure 15.6.What is the deadweight loss resulting from producing at the market equilibrium?
Figure 15.6 shows the market for measles vaccinations, a product whose use generates positive externalities.
-Refer to Figure 15.6.What is the deadweight loss resulting from producing at the market equilibrium?
A) B + C
B) E + C
C) F
D) C
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does a positive externality cause?
A) The marginal social benefit to be equal to the marginal private cost of the last unit produced
B) The marginal social benefit to be less than the marginal private cost of the last unit produced
C) The marginal social benefit to exceed the marginal private cost of the last unit produced
D) The marginal private benefit to exceed the marginal social cost of the last unit produced
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 212
Related Exams