Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Waves begin to "feel bottom" when the depth of water is ________.
A) equal to one-half the wavelength
B) equal to the wavelength
C) twice as great as the wavelength
D) equal to the fetch
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If a spit grows as it is deposited, and extends completely across the former mouth of an estuary, separating it from the open sea, it has become a(n)________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The largest daily tidal range occurs in association with spring tides.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A baymouth bar is an example of "hard stabilization," a feature constructed by people to control wave erosion.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Waves begin to "feel bottom" at a depth that is about one-half their wavelength.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Groins are constructed for the purpose of maintaining or widening beaches that are losing sand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fetch is ________.
A) a method of shoreline erosion control
B) the distance between the trough of a wave and the still water level
C) the circular pattern made by water particles when a wave passes
D) the distance over which the wind blows over open water
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
As the tide rises, water flows in toward the shore as the ebb tide.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One result of wave refraction is that wave energy is concentrated ________.
A) on headlands projecting into the water
B) on tombolos
C) in bays, coves, and other recessed areas between headlands
D) on spits
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Barrier islands are common on the Gulf Coast but rare or absent along the Pacific Coast of the United States.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A(n)________ is a place where fresh and salt water mix, such as a drowned river valley along a submergent coast.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The daily tidal range is of the least magnitude during ________.
A) the daytime
B) spring tides
C) neap tides
D) slack water
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The center of each of Earth's five major gyres is found at about ________ latitude.
A) 0° (the equator)
B) 30°
C) 60°
D) 90°
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
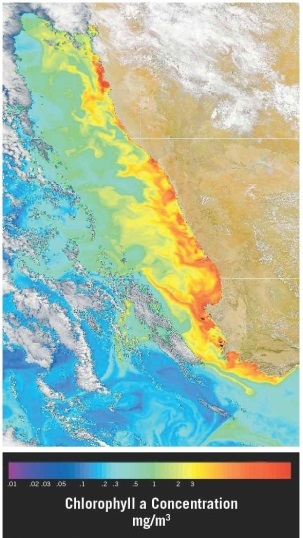 Examine the satellite view of chlorophyll concentrations in the southern Atlantic Ocean along the southwest coast of Africa (the nations of Namibia and South Africa) . Which of the following statements offers the best explanation for the observed pattern(s) ?
Examine the satellite view of chlorophyll concentrations in the southern Atlantic Ocean along the southwest coast of Africa (the nations of Namibia and South Africa) . Which of the following statements offers the best explanation for the observed pattern(s) ?
A) This is an area of downwelling, where water is sinking due to the higher density it gains when sea ice forms and salinity increases.
B) This is an area of upwelling, where nutrient-rich water is rising due to winds blowing over the ocean's surface.
C) This is an area of shallow water and waves breaking as they "feel bottom."
D) The coast is a "dead zone," an area of very low biological activity.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
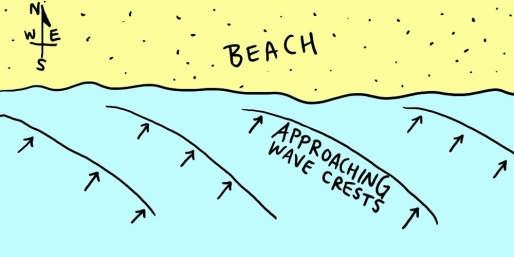 Examine the map shown in the figure. If you were to go swimming in the ocean along this shoreline, which way would the longshore current carry you? ________
Examine the map shown in the figure. If you were to go swimming in the ocean along this shoreline, which way would the longshore current carry you? ________
Correct Answer

verified
east (or "right," de...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
Turbulent water created by breaking waves is known as ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following shoreline features is a result of deposition?
A) barrier island
B) sea stack
C) wave-cut platform
D) marine terrace
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When waves reach shallow water they tend to be ________, which makes them become parallel to the shore.
A) reflected
B) refracted
C) translated
D) eroded
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When viewed from above, the North Atlantic Gyre displays a clockwise sense of motion.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 65
Related Exams