A) 2.0.
B) 12.0.
C) 7.0.
D) 5.0.
E) 9.0.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a freshly prepared 1 M solution of glucose in water. You carefully pour out a 100 mL sample of that solution. How many glucose molecules are included in that 100 mL sample?
A) 6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D) 12.04 × 10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does ice float in liquid water?
A) The high surface tension of liquid water keeps the ice on top.
B) The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking.
C) Ice always has air bubbles that keep it afloat.
D) Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of liquid water.
E) The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the pH of a solution is increased from pH 5 to pH 7, it means that the
A) concentration of H⁺ is twice (2X) what it was at pH 5.
B) concentration of H⁺ is one-half (1/2) what it was at pH 5.
C) concentration of OH⁻ is 100 times greater than what it was at pH 5.
D) concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth (0.01X) what it was at pH 5.
E) concentration of H⁺ is 100 times greater and the concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth what they were at pH 5.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The partial negative charge in a molecule of water occurs because
A) the oxygen atom acquires an additional electron.
B) the electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus.
C) the oxygen atom has two pairs of electrons in its valence shell that are not neutralized by hydrogen atoms.
D) the oxygen atom forms hybrid orbitals that distribute electrons unequally around the oxygen nucleus.
E) one of the hydrogen atoms donates an electron to the oxygen atom.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
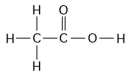 -How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required to make 2.5 L of a 1 M solution? (carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
-How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required to make 2.5 L of a 1 M solution? (carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of a solution with a hydroxyl ion [OH⁻] concentration of 10⁻¹² ᴹ?
A) pH 2
B) pH 4
C) pH 10
D) pH 12
E) pH 14
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the cytoplasm of a cell is at pH 7, and the mitochondrial matrix is at pH 8, this means that
A) the concentration of H⁺ ions is tenfold higher in the cytoplasm than in the mitochondrial matrix.
B) the concentration of H⁺ ions is tenfold higher in the mitochondrial matrix than in the cytoplasm.
C) the concentration of H⁺ ions in the cytoplasm is 7/8 the concentration in the mitochondrial matrix.
D) the mitochondrial matrix is more acidic than the cytoplasm.
E) the concentration of H⁺ ions in the cytoplasm is 8/7 the concentration in the mitochondrial matrix.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You live in Atlantic Canada and you are Skyping a friend in Manitoba. You are both complaining about the weather as both regions are being subjected to the same arctic air mass. As you discuss it, however, it becomes clear that she is experiencing a bitter cold that you are not. You realize that you had pretty much the same conversation last summer when it was much hotter in Manitoba than at home. -We can be sure that a mole of table sugar and a mole of vitamin C are equal in their
A) mass in daltons.
B) mass in grams.
C) volume.
D) number of atoms.
E) number of molecules.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You live in Atlantic Canada and you are Skyping a friend in Manitoba. You are both complaining about the weather as both regions are being subjected to the same arctic air mass. As you discuss it, however, it becomes clear that she is experiencing a bitter cold that you are not. You realize that you had pretty much the same conversation last summer when it was much hotter in Manitoba than at home. -A slice of pizza has 2092 kJ. If we could burn the pizza and use all the heat to warm a 50-L container of cold water, what would be the approximate increase in the temperature of the water? (Note: A litre of cold water weighs about 1 kg.)
A) 50°C
B) 5°C
C) 1°C
D) 100°C
E) 10°C
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The biological significance of water being its densest at 4°C is that
A) bodies of water do not freeze solid.
B) floating ice allows for a solid surface in open water.
C) ice functions as a protective barrier in ponds and lakes.
D) organisms are best adapted to 4°C.
E) oceans are never colder than 4°C.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider two solutions: solution X has a pH of 4; solution Y has a pH of 7. From this information, we can reasonably conclude that
A) solution Y has no free hydrogen ions (H⁺) .
B) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 30 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
C) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y is 1000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X.
D) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 3 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
E) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 1000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is readily soluble in water, according to the equation CO₂ + H₂O ↔ H₂CO₃. Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) is a weak acid. Respiring cells release CO₂ into the bloodstream. What will be the effect on pH of blood as that blood first comes in contact with respiring cells?
A) Blood pH will decrease slightly.
B) Blood pH will increase slightly.
C) Blood pH will remain unchanged.
D) Blood pH will first increase, then decrease as CO₂ combines with hemoglobin.
E) Blood pH will first decrease, then increase sharply as CO₂ combines with hemoglobin.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on identical containers of water and methanol (wood alcohol) , so that each liquid absorbs the same amount of energy minute by minute. The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will happen to the temperature of the water and the methanol?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Water molecules are able to form hydrogen bonds with
A) compounds that have polar covalent bonds.
B) oils.
C) oxygen gas (O₂) molecules.
D) chloride ions.
E) any compound that is not soluble in water.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the pH of a solution is decreased from 9 to 8, it means that the
A) concentration of H⁺ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it was at pH 9.
B) concentration of H⁺ has increased tenfold (10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
C) concentration of OH⁻ has increased tenfold (10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
D) concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it was at pH 9.
E) concentration of H⁺ has increased tenfold (10X) and the concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what they were at pH 9.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A beaker contains 100 mL of NaOH solution at pH = 13. A technician carefully pours into the beaker 10 mL of HCl at pH = 1. Which of the following statements correctly describes the results of this mixing?
A) The concentration of Na⁺ ion rises.
B) The concentration of Cl⁻ ion will be 0.1 M.
C) The concentration of undissociated H₂O molecules remains unchanged.
D) The pH of the beaker's contents will be neutral.
E) The pH of the beaker's contents falls.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrogen bonding in water is a result of
A) the electronegativity of hydrogen atoms.
B) the electronegativity of oxygen creating partially positive hydrogen atoms.
C) the single electron in hydrogen, allowing for covalent bonds with other molecules.
D) the linear shape of the water molecule.
E) the ionic charge of water.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small birthday candle is weighed, then lighted and placed beneath a metal can containing 100 mL of water. Careful records are kept as the temperature of the water rises. Data from this experiment are shown on the graph. What amount of heat energy is released in the burning of candle wax? 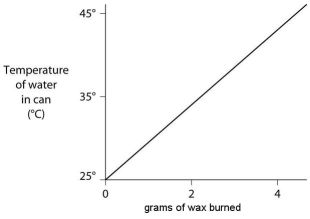
A) 2092 joules per gram of wax burned
B) 20 920 joules per gram of wax burned
C) 41 840 joules per gram of wax burned
D) 83 680 joules per gram of wax burned
E) 209 200 joules per gram of wax burned
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You live in Atlantic Canada and you are Skyping a friend in Manitoba. You are both complaining about the weather as both regions are being subjected to the same arctic air mass. As you discuss it, however, it becomes clear that she is experiencing a bitter cold that you are not. You realize that you had pretty much the same conversation last summer when it was much hotter in Manitoba than at home. -This phenomenon is due to
A) solar energy at different latitudes.
B) evolutionary adaptation to different climates.
C) rate of vaporization.
D) land freezing before water and thus land masses are colder.
E) specific heat of water.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 80
Related Exams