A) Purines pair with pyrimidines.
B) C nucleotides pair with A nucleotides.
C) Deoxyribose sugars bind with ribose sugars.
D) Nucleotides bind with nucleosides.
E) Nucleotides bind with nucleoside triphosphates.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the basis for the difference in how the leading and lagging strands of DNA molecules are synthesized?
A) The origins of replication occur only at the 5' end.
B) Helicases and single-strand binding proteins work at the 5' end.
C) DNA polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3' end of a growing strand.
D) DNA ligase works only in the 3' → 5' direction.
E) Polymerase can work on only one strand at a time.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At a specific area of a chromosome, the sequence of nucleotides below is present where the chain opens to form a replication fork: 3' C C T A G G C T G C A A T C C 5' An RNA primer is formed starting at the underlined T (T) of the template. Which of the following represents the primer sequence?
A) 5' G C C T A G G 3'
B) 3' G C C T A G G 5'
C) 5' A C G T T A G G 3'
D) 5' A C G U U A G G 3'
E) 5' G C C U A G G 3'
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA replication?
A) synthesize RNA nucleotides to make a primer
B) catalyze the lengthening of telomeres
C) join Okazaki fragments together
D) unwind the parental double helix
E) stabilize the unwound parental DNA
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use Figure 16.1 to answer the following questions.
 Figure 16.1
-Eukaryotic telomeres replicate differently than the rest of the chromosome. This is a consequence of which of the following?
Figure 16.1
-Eukaryotic telomeres replicate differently than the rest of the chromosome. This is a consequence of which of the following?
A) The evolution of telomerase enzyme
B) DNA polymerase that cannot replicate the leading strand template to its 5' end
C) Gaps left at the 5' end of the lagging strand because of the need for a 3' onto which nucleotides can attach
D) Gaps left at the 3' end of the lagging strand because of the need for a primer
E) The "no ends" of a circular chromosome
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Polytene chromosomes of Drosophila salivary glands each consist of multiple identical DNA strands that are aligned in parallel arrays. How could these arise?
A) replication followed by mitosis
B) replication without separation
C) meiosis followed by mitosis
D) fertilization by multiple sperm
E) special association with histone proteins
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It became apparent to Watson and Crick after completion of their model that the DNA molecule could carry a vast amount of hereditary information in which of the following?
A) sequence of bases
B) phosphate-sugar backbones
C) complementary pairing of bases
D) side groups of nitrogenous bases
E) different five-carbon sugars
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an experiment, DNA is allowed to replicate in an environment with all necessary enzymes, dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and radioactively labeled dTTP (³H thymidine) for several minutes and then switched to nonradioactive medium. It is then viewed by electron microscopy and autoradiography. The drawing below represents the results. 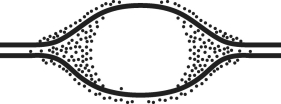 Grains represent radioactive material within the replicating eye.
Figure 16.2
Which is the most likely interpretation?
Grains represent radioactive material within the replicating eye.
Figure 16.2
Which is the most likely interpretation?
A) There are two replication forks going in opposite directions.
B) Thymidine is only being added where the DNA strands are furthest apart.
C) Thymidine is only added at the very beginning of replication.
D) Replication proceeds in one direction only.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a science fair project, two students decided to repeat the Hershey and Chase experiment, with modifications. They decided to label the nitrogen of the DNA, rather than the phosphate. They reasoned that each nucleotide has only one phosphate and two to five nitrogens. Thus, labeling the nitrogens would provide a stronger signal than labeling the phosphates. Why won't this experiment work?
A) There is no radioactive isotope of nitrogen.
B) Radioactive nitrogen has a half-life of 100,000 years, and the material would be too dangerous for too long.
C) Avery et al. have already concluded that this experiment showed inconclusive results.
D) Although there are more nitrogens in a nucleotide, labeled phosphates actually have 16 extra neutrons; therefore, they are more radioactive.
E) Amino acids (and thus proteins) also have nitrogen atoms; thus, the radioactivity would not distinguish between DNA and proteins.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A biochemist isolates and purifies various molecules needed for DNA replication. When she adds some DNA, replication occurs, but each DNA molecule consists of a normal strand paired with numerous segments of DNA a few hundred nucleotides long. What has she probably left out of the mixture?
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) nucleotides
D) Okazaki fragments
E) primase
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Individuals with the disorder xeroderma pigmentosum are hypersensitive to sunlight. This occurs because their cells have which impaired ability?
A) They cannot replicate DNA.
B) They cannot undergo mitosis.
C) They cannot exchange DNA with other cells.
D) They cannot repair thymine dimers.
E) They do not recombine homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In trying to determine whether DNA or protein is the genetic material, Hershey and Chase made use of which of the following facts?
A) DNA contains sulfur, whereas protein does not.
B) DNA contains phosphorus, but protein does not.
C) DNA contains nitrogen, whereas protein does not.
D) DNA contains purines, whereas protein includes pyrimidines.
E) RNA includes ribose, while DNA includes deoxyribose sugars.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use Figure 16.1 to answer the following questions.
 Figure 16.1
-An Okazaki fragment has which of the following arrangements?
Figure 16.1
-An Okazaki fragment has which of the following arrangements?
A) primase, polymerase, ligase
B) 3' RNA nucleotides, DNA nucleotides 5'
C) 5' RNA nucleotides, DNA nucleotides 3'
D) DNA polymerase I, DNA polymerase III
E) 5' DNA to 3'
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a nucleosome, the DNA is wrapped around
A) polymerase molecules.
B) ribosomes.
C) histones.
D) a thymine dimer.
E) satellite DNA.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mendel and Morgan did not know about the structure of DNA; however, which of the following of their contributions was (were) necessary to Watson and Crick?
A) the particulate nature of the hereditary material
B) dominance vs. recessiveness
C) sex-linkage
D) genetic distance and mapping
E) the usefulness of peas and Drosophila
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his transformation experiments, what did Griffith observe?
A) Mutant mice were resistant to bacterial infections.
B) Mixing a heat-killed pathogenic strain of bacteria with a living nonpathogenic strain can convert some of the living cells into the pathogenic form.
C) Mixing a heat-killed nonpathogenic strain of bacteria with a living pathogenic strain makes the pathogenic strain nonpathogenic.
D) Infecting mice with nonpathogenic strains of bacteria makes them resistant to pathogenic strains.
E) Mice infected with a pathogenic strain of bacteria can spread the infection to other mice.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that
A) the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs within individuals of a species.
B) the human genome is more complex than that of other species.
C) the amount of A is always equivalent to T, and C to G.
D) the amount of ribose is always equivalent to deoxyribose.
E) transformation causes protein to be brought into the cell.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In prophase I of meiosis in female Drosophila, studies have shown that there is phosphorylation of an amino acid in the tails of histones. A mutation in flies that interferes with this process results in sterility. Which of the following is the most likely hypothesis?
A) These oocytes have no histones.
B) Any mutation during oogenesis results in sterility.
C) Phosphorylation of all proteins in the cell must result.
D) Histone tail phosphorylation prohibits chromosome condensation.
E) Histone tails must be removed from the rest of the histones.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A typical bacterial chromosome has ~4.6 million nucleotides. This supports approximately how many genes?
A) 4.6 million
B) 4.4 thousand
C) 45 thousand
D) about 400
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can be determined directly from X-ray diffraction photographs of crystallized DNA?
A) the diameter of the helix
B) the rate of replication
C) the sequence of nucleotides
D) the bond angles of the subunits
E) the frequency of A vs. T nucleotides
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 72
Related Exams