A) 6,5
B) 6,6
C) 5,6
D) 5,5
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the correct description from this list for the following terms: -major proteoglycan of cartilage
A) nodulation factor
B) H antigen (blood groups)
C) hyaluronic acid
D) aggrecan
E) bacterial cell wall (peptidoglycan)
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Anomers can be interconverted ________.
A) by rotation about carbon-carbon bonds
B) via a linear intermediate
C) by an isotopic exchange reaction
D) None of the above.Anomers cannot be interconverted.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Examine the Fischer projection below.How is this carbohydrate classified? 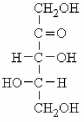
A) L enantiomer;aldopentose.
B) L enantiomer;ketopentose.
C) D enantiomer;aldohexose.
D) D enantiomer;ketopentose.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of bond links the monomers of a polysaccharide?
A) Glucotide bond.
B) Phosphate ester bond.
C) Peptide bond.
D) Glycosidic bond.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a similarity between glycogen and amylopectin?
A) They each contain about 6000 glucose residues.
B) Each has one reducing end and many nonreducing ends.
C) Each is highly branched.
D) Each has branches of similar chain length.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
α-amylases hydrolyze α(1→4)linkages and β-amylases hydrolyze β(1→4)linkages,but neither attack α1→6)linkages.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monosaccharide whose anomeric carbon atom has a glycosidic bond to an alcohol,amine or thiol is a ________.
A) glycoside
B) glycoprotein
C) heteroglycan
D) glucoconjugate
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Examine the cyclic D-monosaccharide shown below.The ring structure is the ________ and the linear form of this monosaccharide must be a(n) ________. 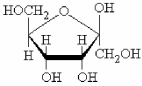
A) α anomer;ketose
B) β anomer;ketose
C) α anomer;aldose
D) β anomer;aldose
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The elasticity and resistance to compression of connective tissue is due to
A) the branching of the glycosaminoglycans there.
B) the glycosidic linkage to the serine of proteins in the glycosaminoglycans.
C) the carboxyl and sulfated groups in the glycosaminoglycans.
D) the rigid structure of the glycosaminoglycans.
E) All of the above.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The main difference between structures of amylopectin and glycogen is the specific sugar subunit.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which does not apply to dihydroxyacetone?
A) Ketose.
B) Triose.
C) Chiral.
D) Water-soluble.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For cattle,cellulose is a storage homoglycan.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monosaccharide derivatives in which an amino group replaces one of the hydroxyl groups may have important roles in
A) DNA structure.
B) intermediary metabolisms.
C) vitamin C.
D) sialic acids.
E) All of the above.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Fischer projections of linear D-glucose and D-galactose are shown below.These two molecules are ________. 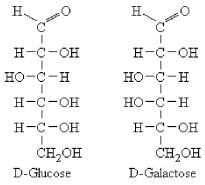
A) epimers
B) enantiomers
C) anomers
D) structural (constitutional) isomers
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is a general term indicating a carbohydrate polymer?
A) Glycan.
B) Polycarb.
C) Multimer.
D) Oligosaccharide.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a glycoconjugate?
A) Proteoglycan.
B) Glycolipid.
C) Glycoprotein.
D) Homoglycan.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a sugar polymer is analyzed and found to have equal portions of reducing and non-reducing ends,it is likely that
A) it shows directionality.
B) it is linear.
C) it is branched.
D) it is branched,but not very highly.
E) some of the internal glycosidic bonds are in equilibrium with open chain forms.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The chair conformation of furanoses is generally preferred to minimize steric repulsion.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is false about the sugar units in DNA?
A) They are cyclic in DNA.
B) It is a deoxy form of ribose.
C) It is an epimer of glucose.
D) It has a D-configuration.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 92
Related Exams