A) production decreased to Q₂.
B) production increased to Q₄.
C) this product were no longer produced.
D) output stayed at Q₃.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that smoking creates a negative externality.If the government imposes a per-cigarette tax equal to the per-cigarette externality,then
A) the equilibrium quantity of cigarettes smoked will be less than the socially optimal quantity of cigarettes smoked.
B) the equilibrium quantity of cigarettes smoked will be greater than the socially optimal quantity of cigarettes smoked.
C) the equilibrium quantity of cigarettes smoked will equal the socially optimal quantity of cigarettes smoked.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that smoking creates a negative externality.If the government does not interfere in the cigarette market,then
A) the equilibrium quantity of cigarettes smoked will equal the socially optimal quantity of cigarettes smoked.
B) the equilibrium quantity of cigarettes smoked will be greater than the socially optimal quantity of cigarettes smoked.
C) the equilibrium quantity of cigarettes smoked will be less than the socially optimal quantity of cigarettes smoked.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that electricity producers create a negative externality equal to $5 per unit.Further suppose that the government gives a $5 per-unit subsidy to producers.What is the relationship between the equilibrium quantity and the socially optimal quantity of electricity to be produced?
A) They are equal.
B) The equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
C) The equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An externality
A) is a type of market failure.
B) causes markets to allocate resources efficiently.
C) strengthens the role of the "invisible hand" in the marketplace.
D) affects producers but not consumers.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a positive externality?
A) A college student buys a new car when she graduates.
B) The mayor of a small town plants flowers in the city park.
C) Local high school teachers have pizza delivered every Friday for lunch.
D) An avid fisherman buys new fishing gear for his next fishing trip.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an advantage of corrective taxes?
A) They raise revenues for the government.
B) They enhance economic efficiency.
C) They subsidize the production of goods with positive externalities.
D) They move the allocation of resources closer to the social optimum.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since restored historic buildings convey a positive externality,local governments may choose to
A) regulation the demolition of them.
B) provide tax breaks to owners who restore them.
C) increase property taxes in historic areas.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-4
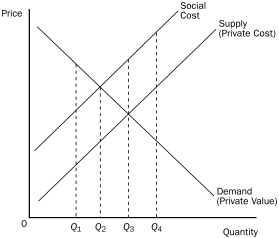 -Refer to Figure 10-4.The socially optimal quantity would be
-Refer to Figure 10-4.The socially optimal quantity would be
A) Q₁.
B) Q₂.
C) Q₃.
D) Q₄.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In many cases the Coase theorem does not work well because
A) there are too few parties at the negotiation table.
B) the government does not know about the Coase theorem.
C) transaction costs are too high.
D) transaction costs are too low.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This figure reflects the market for outdoor concerts in a public park surrounded by residential neighborhoods.
Figure 10-3
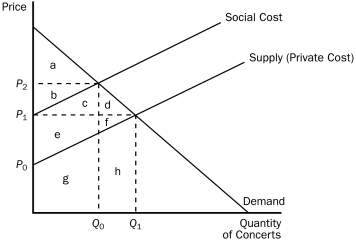 -Refer to Figure 10-3.At the private market outcome,the equilibrium price will be
-Refer to Figure 10-3.At the private market outcome,the equilibrium price will be
A) P₀.
B) P₁.
C) P₂.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Barking dogs cannot be considered an externality because externalities must be associated with some form of market exchange.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-2
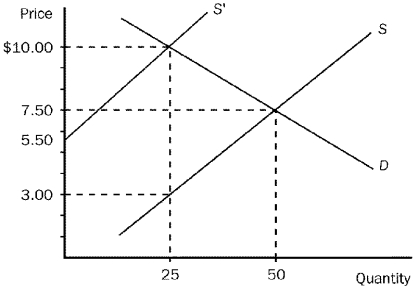 -Refer to Figure 10-2.Suppose that the production of soccer balls creates a social cost which is depicted in the graph above.Without any government regulation,how many soccer balls will be produced?
-Refer to Figure 10-2.Suppose that the production of soccer balls creates a social cost which is depicted in the graph above.Without any government regulation,how many soccer balls will be produced?
A) 3
B) 10
C) 25
D) 50
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a beekeeper places his hives of bees in an orchard so that the bees can gather nectar to produce honey,the bees pollinate the orchard,which increases the yield of fruit.This benefits
A) only the beekeeper.
B) the beekeeper, but it creates a negative externality because the bees are a hazard to the orchard owner.
C) only the owner of the orchard.
D) both the beekeeper and the orchard owner.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both pollution permits and corrective taxes are viewed as cost effective ways to keep the environment clean.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government chooses a policy that aligns private incentives with social efficiency to solve an externality problem,it
A) provides incentives to private decisionmakers to induce them to solve the externality problem on their own.
B) typically uses command-and-control techniques.
C) uses taxes more often than subsidies.
D) uses subsidies more often than taxes.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that flower gardens create a positive externality equal to $1 per plant.Further suppose that the local government offers a $1 per-plant subsidy to growers.What is the relationship between the equilibrium quantity and the socially optimal quantity of plants grown?
A) The equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
B) The equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
C) They are equal.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that your roommate is very messy.Suppose she gets a $100 benefit from being messy but imposes a $200 cost on you.The Coase theorem would suggest that an efficient solution would be for you to
A) pay your roommate at least $100 but no more than $200 to clean up after herself.
B) pay your roommate at least $201 to clean up after herself.
C) charge your roommate at least $100 to have you clean up after her.
D) charge your roommate at least $200 but no more than $300 to keep you from complaining about the mess.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Taxes are more difficult to administer than regulations.
B) Taxes provide incentives for firms to adopt new methods to reduce negative externalities.
C) Command-and-control policies provide incentives for private decisionmakers to solve their problems on their own.
D) Corrective taxes distort incentives.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following require firms to pay to pollute? (i) corrective taxes (ii) tradable pollution permits (iii) pollution regulations
A) (i) only
B) both (i) and (ii)
C) (iii) only
D) both (ii) and (iii)
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 288
Related Exams