A) they block the active site of enzymes so that inhibitors cannot bind.
B) they can act as Lewis acids.
C) water is excluded from the active site when metal ions are bound.
D) they prevent protein aggregation.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the concerted model of allosteric behavior, an allosteric activator
A) favors the taut (tight) form of the enzyme.
B) favors the relaxed form of the enzyme.
C) can only bind to the enzyme if the substrate is already bound.
D) can only bind to the enzyme if the substrate has not already bound.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An important step in elucidating the behavior of an enzyme is
A) obtaining a crystalline sample of the enzyme.
B) insuring that metal ions are always excluded from the enzyme sample.
C) determining the active site residues.
D) none of these
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A velocity curve (V vs. [S]) for a typical allosteric enzyme will be
A) a rectangular hyperbola.
B) a sigmoid curve.
C) a straight line.
D) a parabola.
E) none of these
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Homotrophic effects for allosteric enzymes involve
A) the same molecule binding to different sites in the enzyme.
B) different molecules binding to the same site in an enzyme.
C) different molecules binding to different sites in the same enzyme.
D) All of these are homotrophic effects.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
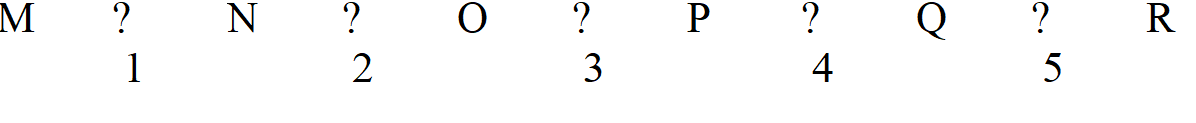 -Refer to Exhibit 7A. Which two enzymes would be the most likely ones to regulate if this pathway is freely reversible and can go both ways?
-Refer to Exhibit 7A. Which two enzymes would be the most likely ones to regulate if this pathway is freely reversible and can go both ways?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 1 and 5
D) 2 and 4
E) 4 and 5
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which groups of amino acids are most likely to be found in the active site of an enzyme?
A) leucine, lysine, alanine.
B) cysteine, isoleucine, phenylalanine.
C) tyrosine, threonine, leucine.
D) serine, histidine, aspartate.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
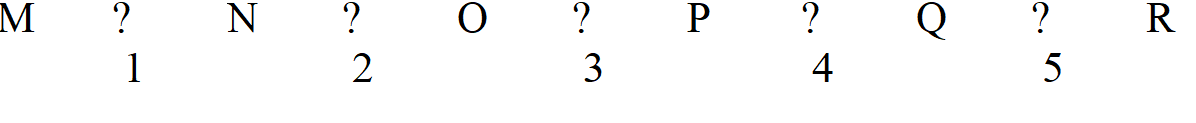 -Refer to Exhibit 7A. The final product, R, will most likely inhibit which reaction?
-Refer to Exhibit 7A. The final product, R, will most likely inhibit which reaction?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of amino acids in an active site is least likely to be involved in enzyme catalysis?
A) Those with hydrophilic, neutral side-chains.
B) Those with negatively charged side-chains.
C) Those with positively charge side-chains.
D) Those with hydrocarbon side-chains.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ATP is a negative allosteric effector for glycogen phosporylase. This is an example of
A) feedback inhibition.
B) positive cooperativity.
C) negative cooperativity.
D) competitive inhibition.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pH profile of an enzyme can help identify specific amino acids in the active site because:
A) all enzymes have a pH optimum
B) only the active site amino acids can detect changes in pH
C) acidic and basic amino acids are often involved in the active site and pH changes can change their ability to catalyze a reaction
D) the pH optimum is always the pI of the most critical amino acid in the active site
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Redox reactions often use this cofactor:
A) Riboflavin
B) Lipoic acid
C) Pyridoxal
D) Thiamine
E) Biotin
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Important mechanisms of enzymatic catalysis include
A) nucleophilic reactions
B) general acid-base catalysis
C) Lewis acid-base catalysis
D) all of these
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes negative cooperativity?
A) Binding of one substrate molecule prevents the enzyme from working at all.
B) Binding of one substrate molecule inhibits the binding of a second substrate.
C) Binding of one substrate molecule enhances the binding of a second substrate.
D) Binding of one substrate molecule inhibits the binding of other effectors.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about coenzymes is true?
A) They are commonly derived from vitamins.
B) They bind to the active site region on specific types of enzymes.
C) They can be metal ions, such as Zn(II) .
D) NAD+, FAD and biotin are all examples of coenzymes.
E) All of these statements are true.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Enzymes that catalyze similar functions will invariably have
A) similar overall structures.
B) serine in their active sites.
C) histidine in their active sites.
D) active sites that can catalyze the reactions in question.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main distinguishing feature of the concerted model for the behavior of allosteric enzymes is that
A) the conformation of all subunits changes simultaneously.
B) it applies only to dimeric enzymes.
C) it involves three possible conformations for all subunits.
D) the T and R conformations exist in roughly equal amounts.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The term K0.5 is analogous to the KM
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where do allosteric inhibitors bind on an enzyme?
A) They always bind at a site different from the active site.
B) They always bind at the active site.
C) They can bind at either active site or another site.
D) They always bind directly to the substrate
E) none of these
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Is the Michaelis-Menten equation useful when studying allosteric enzymes?
A) Yes
B) No
C) Only if the enzyme displays positive cooperativity.
D) Only if the enzyme displays negative cooperativity.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 81
Related Exams