A) a more advanced cerebellum.
B) a cerebellum with several flat layers.
C) a pallium with neurons clustered into nuclei.
D) microvilli to increase the brain's surface area.
E) a large hindbrain
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increased activity in the sympathetic nervous system leads to
A) decreased heart rate.
B) increased secretion by the pancreas.
C) increased secretion by the gallbladder.
D) increased contraction of the stomach.
E) relaxation of the airways in the lungs.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an individual did not possess the NMDA or AMPA receptors,this would inhibit
A) dreaming during sleep.
B) short-term memory.
C) long-term potentiation.
D) motor capacity.
E) short-term potentiation.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following illustration of the limbic system to help answer the next few questions.
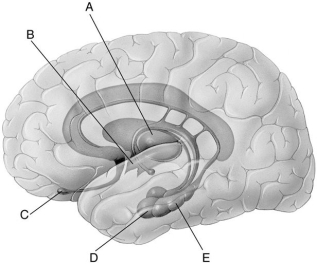 -In the figure,which letter points to the hypothalamus?
-In the figure,which letter points to the hypothalamus?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Our understanding of mental illness has been most advanced by discoveries involving
A) the degree of convolutions in the brain's surface.
B) the evolution of the telencephalon.
C) the sequence of developmental specialization.
D) the chemicals involved in brain communications.
E) the nature of the blood-brain barrier.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures are correctly paired?
A) forebrain and medulla oblongata
B) forebrain and cerebellum
C) midbrain and cerebrum
D) hindbrain and cerebellum
E) brainstem and anterior pituitary gland
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Myelinated neurons are especially abundant in the
A) grey matter of the brain and the white matter of the spinal cord.
B) white matter of the brain and the grey matter of the spinal cord.
C) grey matter of the brain and the grey matter of the spinal cord.
D) white matter in the brain and the white matter in the spinal cord.
E) all areas of the brain and spinal cord.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cephalization,the clustering of neurons and interneurons in the anterior part of the animal,is apparent in
A) Hydra.
B) cnidarians.
C) Planaria.
D) sea stars.
E) invertebrate animals with radial symmetry.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bottlenose dolphins breathe air but can sleep in the ocean because
A) they cease breathing while sleeping and remain underwater.
B) they sleep for only 30 minutes at a time, which is the maximum interval they can cease breathing.
C) they fill their swim bladder with air to keep their blowholes above the surface of the water while they sleep.
D) they move to shallow water to sleep, so they do not need to swim to keep their blowholes above the surface of the water.
E) they alternate which half of their brains is asleep and which half is awake.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hormones that are secreted by the posterior pituitary gland are made in the
A) cerebrum.
B) cerebellum.
C) thalamus.
D) hypothalamus.
E) medulla oblongata.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Central coordination of vertebrate biological rhythms in physiology and behaviour reside in the
A) pituitary gland.
B) hypothalamus.
C) cerebrum.
D) cerebellum.
E) thalamus.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the next few questions. While deployed to Afghanistan,a soldier steps on a landmine and loses the lower portion of his right leg and also sustains a substantial brain injury.In time,doctors observe that the soldier is not acquiring new long-term memories since the explosion occurred; however,his recollection of times previous to the explosion is impeccable.Sometimes the soldier can feel a tingling sensation in his missing limb. -Over time,the soldier's phantom limb syndrome subsides and he rarely "feels" his missing limb.This is an example of
A) neural plasticity.
B) somatosensory regeneration.
C) autonomic arousal.
D) reticular formation.
E) sympathetic response.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly describes the how memories are stored and learning takes place?
A) Memory and learning is related to changes in the degree of myelination of axons.
B) Memory and learning results in an increase in the diameter of axons.
C) Memory and learning results in a shift from aerobic to anaerobic respiration in neurons.
D) Memory and learning involves two types of glutamate receptors.
E) Memory and learning involves stronger action potentials.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly describes the brain reward system?
A) The brain reward system represents an emergent brain property that has arisen independent of natural selection.
B) The brain reward system is a reflex of the peripheral nervous primarily under autonomic control.
C) The brain reward system is housed in the thalamus and primarily regulates the enteric division of the autonomic nervous system.
D) The brain reward system utilizes the neurotransmitter dopamine and is affected by drug addiction.
E) The brain reward system results in the death of neurons during addiction.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The system that modulates excitation and inhibition of smooth and cardiac muscles of the digestive,cardiovascular,and excretory systems is the
A) central nervous system.
B) peripheral nervous system.
C) autonomic nervous system.
D) parasympathetic nervous system.
E) sympathetic nervous system.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The activation of the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system is associated with
A) resting and digesting.
B) release of epinephrine into the blood.
C) increased metabolic rate.
D) fight-or-flight responses.
E) intensive aerobic exercise.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The blood-brain barrier
A) is formed by tight junctions.
B) is formed by oligodendrocytes.
C) tightly regulates the intracellular environment of the CNS.
D) uses chemical signals to communicate with the spinal cord.
E) provides support to the brain tissue.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Preparation for the fight-or-flight response includes activation of the ________ nervous system.
A) sympathetic
B) somatic
C) central
D) visceral
E) parasympathetic
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After suffering a stroke,a patient can see objects anywhere in front of him but pays attention only to objects in his right field of vision.When asked to describe these objects,he has difficulty judging their size and distance.What part of the brain was likely damaged by the stroke?
A) the left frontal lobe
B) the right frontal lobe
C) the left parietal lobe
D) the right parietal lobe
E) the corpus callosum
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The endogenous nature of biological rhythms is based on the observations that animals isolated from light and dark cues
A) continue to have cycles of exactly 24 hours' duration.
B) continue to have cycles of approximately 24 hours' duration; some more rapid, some slower.
C) synchronize activity with whatever lighting cycle is imposed on them.
D) cease having any rhythms.
E) are independent of any genetic determinants.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 85
Related Exams