A) the study of compounds made only by living cells.
B) the study of carbon compounds.
C) the study of vital forces.
D) the study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds.
E) the study of hydrocarbons.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
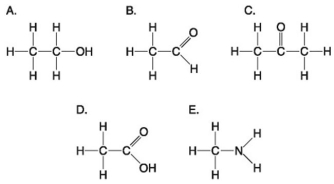 -Which molecule shown above contains a carboxyl group?
-Which molecule shown above contains a carboxyl group?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the following questions based on the figure below.
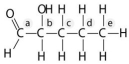 -Which of the following is true of carbon?
-Which of the following is true of carbon?
A) It forms only polar molecules.
B) It can form a maximum of three covalent bonds with other elements.
C) It is highly electronegative.
D) It can form both polar and nonpolar bonds.
E) It can form ionic bonds.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
 -Which molecules shown above contain a carbonyl group?
-Which molecules shown above contain a carbonyl group?
A) A and B
B) B and C
C) B, C, and D
D) D and E
E) E and A
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
A) ketone and methyl
B) carbonyl and amino
C) carboxyl and amino
D) amino and sulfhydryl
E) hydroxyl and carboxyl
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are carbon's most frequent bonding partners?
A) H, N, O
B) H, N, S
C) H, O, S
D) N, O, S
E) H, N, O, S
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is carbon so important in biology?
A) It is a common element on Earth.
B) It has very little electronegativity, making it a good electron donor.
C) It bonds to only a few other elements.
D) It can form a variety of carbon skeletons and host functional groups.
E) It can be part of either hydrophobic or hydrophilic molecules.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Organic molecules with only hydrogens and five carbon atoms can have different structures in all of the following ways except
A) by branching of the carbon skeleton.
B) by varying the number of double bonds between carbon atoms.
C) by varying the position of double bonds between carbon atoms.
D) by forming a ring.
E) by forming enantiomers.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water?
A) The majority of their bonds are polar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
B) The majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
C) They are hydrophilic.
D) They exhibit considerable molecular complexity and diversity.
E) They are lighter than water.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between these two sugar molecules:
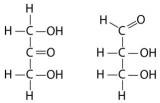
A) structural isomers
B) cis-trans isomers
C) enantiomers
D) isotopes
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many electron pairs does carbon share in order to complete its valence shell?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
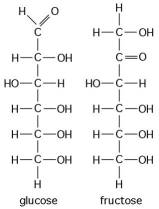 -The figure above shows the structures of glucose and fructose.These two molecules are
-The figure above shows the structures of glucose and fructose.These two molecules are
A) geometric isotopes.
B) enantiomers.
C) cis-trans isomers.
D) structural isomers.
E) nonisotopic isomers.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the following questions based on the figure below.
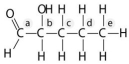 -Which action could produce a carbonyl group?
-Which action could produce a carbonyl group?
A) the replacement of the -OH of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
B) the addition of a thiol to a hydroxyl
C) the addition of a hydroxyl to a phosphate
D) the replacement of the nitrogen of an amine with oxygen
E) the addition of a sulfhydryl to a carboxyl
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three or four of the following illustrations depict different structural isomers of the organic compound with molecular formula C₆H₁₄.For clarity,only the carbon skeletons are shown; hydrogen atoms that would be attached to the carbons have been omitted.Which one,if any,is not a structural isomer of this compound?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) Each of the illustrations in the other answer choices depicts a structural isomer of the compound with molecular formula C₆H₁₄.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrocarbons are ________ because most of their bonds are ________ carbon-hydrogen links.
A) hydrophilic; polar
B) hydrophilic; charged
C) hydrophobic; polar
D) hydrophobic; non-polar
E) inorganic; not
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
 -Which molecule shown above would have a positive charge in aqueous solution at pH 7?
-Which molecule shown above would have a positive charge in aqueous solution at pH 7?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes cis-trans isomers?
A) They have variations in arrangement around a double bond.
B) They have an asymmetric carbon that makes them mirror images.
C) They have the same chemical properties.
D) They have different molecular formulas.
E) Their atoms and bonds are arranged in different sequences.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
L-dopa and D-dopa,shown below,are an example of a pharmaceutical drug that occurs as enantiomers,or molecules that
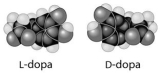
A) have identical three-dimensional shapes.
B) are mirror images of one another.
C) are structural isomers.
D) are mirror images of one another and are likely to have the same biological activity.
E) are cis-trans isomers.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
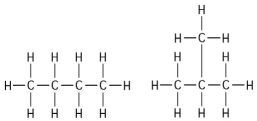 -The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
-The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
A) optical isomers.
B) enantiomers.
C) structural isomers.
D) cis-trans isomers.
E) chain length isomers.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
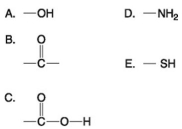 -Which of the groups above is a carboxyl functional group?
-Which of the groups above is a carboxyl functional group?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 86
Related Exams