A) mirror-image, nonsuperimposable stereoisomers.
B) non-mirror-image, nonsuperimposable stereoisomers.
C) stereoisomers with one or more double bonds.
D) none of the above.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following monosaccharides is an aldose
A) glucose
B) galactose
C) mannose
D) ribose
E) all of them
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following artificial sweeteners is a chemical derivative of sucrose?
A) saccharin
B) cyclamates
C) sucralose
D) aspartame
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16A A carbohydrate Fischer projection. 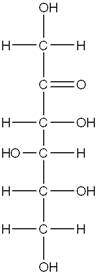 Refer to Exhibit 16BA Which of the following figures represents the Haworth projection of the carbohydrate shown?
Refer to Exhibit 16BA Which of the following figures represents the Haworth projection of the carbohydrate shown?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following sugar is also called milk sugar:
A) Fructose
B) Glucose
C) Lactose
D) Sucrose
E) Maltose
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning sugar polymers is false ?
A) Branched polymers have one non-reducing end and many reducing ends.
B) Linear polymers are more water-soluble than branched ones.
C) Branched polymers are more water-soluble than linear ones.
D) Sugar polymers may vary both in the composition of the sugar monomers and in the types of connecting glycosidic bonds.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major difference between amylose and amylopectin is that
A) amylose is connected by α (1 − 4) bonds and amylopectin is connected by β (1 − 4) bonds.
B) amylose is branched and amylopectin is not.
C) amylopectin is branched and amylose is not.
D) each is composed different types of sugar residues.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Maltose is composed of the following simple sugars
A) galactose only
B) glucose only
C) fructose only
D) galactose and glucose
E) glucose and fructose
F) galactose and fructose
H) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between cellobiose and maltose is:
A) one contains glucose and the other fructose
B) they contain different monosaccharides
C) they both contain glucose units but are connected together at different carbons
D) one has an á linkage and the other a â linkage
E) there is no difference between the two
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Blood typing depends on
A) the nature of the oligosaccharide portion of glycoproteins on the surface of red blood cells
B) the presence of a polysaccharide coating on red blood cells
C) the presence of a polysaccharide coating on white blood cells
D) the addition of sucrose to blood before storage
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aldoses can form which type of cyclic structure?
A) Hemiacetal
B) Hemiketal
C) Both hemiacetal and hemiketal
D) Neither hemiacetal and hemiketal
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16B 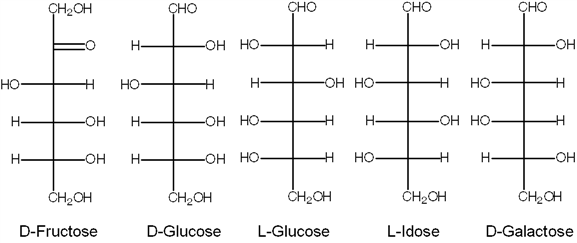 Refer to Exhibit 16B. Epimers of D-Glucose include:
Refer to Exhibit 16B. Epimers of D-Glucose include:
A) D-Fructose and L-Glucose
B) D-Glucose and L-Glucose
C) L-Glucose and L-Idose
D) L-Idose and D-Galactose
E) L-Glucose and D-Galactose
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following sugar is also called blood sugar:
A) Fructose
B) Glucose
C) Lactose
D) Sucrose
E) Maltose
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One advantage of branched sugar polymers is the availability of more ends for chemical reaction.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Insoluble fiber in the diet is better at better at providing bulk and stimulating peristaltic action than soluble fiber.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16B 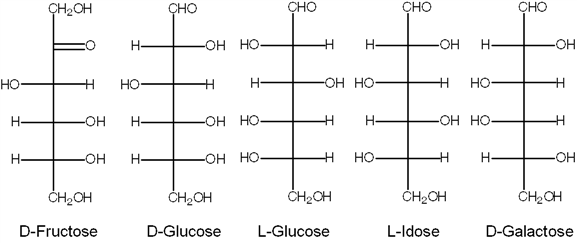 Refer to Exhibit 16B. The enantiomer of D-glucose is:
Refer to Exhibit 16B. The enantiomer of D-glucose is:
A) D-Fructose
B) D-Glucose
C) L-Glucose
D) L-Idose
E) D-Galactose
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cellulose is indigestible to most animals because
A) animals do not have the enzymes needed to hydrolyze ester linkages between the monomer units
B) animals do not have the enzymes needed to hydrolyze the α -glycosidic linkages between the monomer units
C) animals do not have the enzymes needed to hydrolyze the β -glycosidic linkages between the monomer units
D) its molecular weight is too high for it to be degraded by enzymes
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glycogen is
A) polysaccharide storage polymer found in plants
B) a linear polysaccharide
C) a highly branched polysaccharide found in animals
D) a synthetic sugar substitute
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lactose intolerance
A) arises from inability to metabolize the disaccharide lactose
B) depends on a deficiency of sucrose in the diet
C) is based on the composition of lactose, consisting glucose and fructose in glycosidic linkage
D) arises because lactose is a dimer of galactose
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a D-sugar, any group that is written to the right of the carbon in a Fischer projection
A) has an upward projection in a Haworth projection.
B) has a downward projection in a Haworth projection.
C) may be either up or down in a Haworth projection, it depends on the individual sugar.
D) is missing from a Haworth projection.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 97
Related Exams