A) catabolism (catabolic pathways)
B) metabolism
C) anabolism (anabolic pathways)
D) dehydration
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules is most similar in structure to ATP?
A) a pentose sugar
B) a DNA nucleotide
C) an RNA nucleotide
D) an amino acid with three phosphate groups attached
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Zinc is an essential trace element for most organisms. Zinc is required in the active site of the enzyme carboxypeptidase where it most likely functions in which of the following ways?
A) as a noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme
B) as an allosteric activator of the enzyme
C) as a cofactor necessary for enzyme activity
D) as a coenzyme derived from a vitamin
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes metabolism in its entirety in all organisms?
A) Metabolism depends on a constant supply of energy from food.
B) Metabolism uses all of an organism's resources.
C) Metabolism consists of all the energy transformation reactions in an organism.
D) Metabolism manages the increase of entropy in an organism.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Students conducting research observe the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction under various conditions with a fixed amount of enzyme in each sample. When will increasing the substrate concentration likely result in the greatest increase in the reaction rate?
A) when a cofactor is required in the reaction
B) when an allosteric inhibitor is present in the reaction
C) when a noncompetitive inhibitor is present in the reaction
D) when a competitive inhibitor is present in the reaction
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In addition to activating or inhibiting enzymes through allosteric regulation, which of these mechanisms do cells also use to control enzymatic activity?
A) localization of enzymes into specific organelles or membranes
B) secretion of enzymes out of the cell
C) assembly of enzymes into large aggregates
D) altering internal pH
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Penicillin is an antibiotic that kills bacteria by binding to the active site of an enzyme involved in synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Which of the following phenomena best describes the mechanism of action of penicillin?
A) noncompetitive inhibition
B) feedback inhibition
C) allosteric regulation
D) competitive inhibition
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A clasping handshake may be used as an analogy for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction because it represents the specific manner in which an enzyme ________.
A) folds to form secondary and tertiary structures
B) interacts with water
C) binds substrate
D) is denatured by low pH
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme is composed of four identical subunits. Binding of substrate to one subunit stimulates more rapid binding of substrate to each of the other three subunits. This enzyme is most likely regulated by which of the following mechanisms?
A) noncompetitive inhibition
B) competitive activation
C) competitive inhibition
D) cooperativity
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
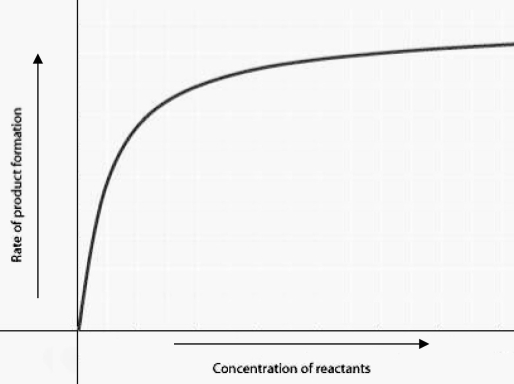 The figure displays the relationship between initial rate of product formation and reactant concentration in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with a fixed amount of enzyme. Which of the following statements best explains the shape of the rate curve at high reactant concentration?
The figure displays the relationship between initial rate of product formation and reactant concentration in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with a fixed amount of enzyme. Which of the following statements best explains the shape of the rate curve at high reactant concentration?
A) Feedback inhibition by product occurs at high reactant concentrations.
B) Most enzyme molecules are occupied by substrate at high reactant concentrations.
C) The reaction nears equilibrium at high reactant concentrations.
D) The rate of the reverse reaction increases at high reactant concentrations.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to ________.
A) add more of the enzyme
B) heat the solution to 90°C
C) add more substrate
D) add a noncompetitive inhibitor
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below. 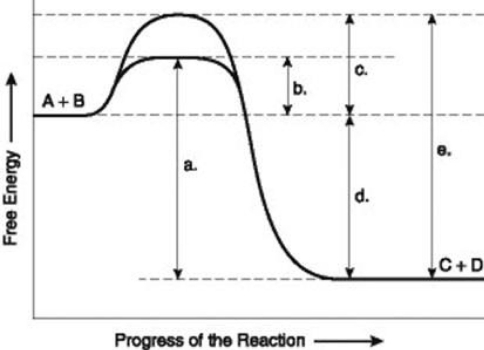 The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the lower-case letters in the figure represents a free energy change that would be the same in either an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction?
The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the lower-case letters in the figure represents a free energy change that would be the same in either an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following examples describes a type of potential rather than kinetic energy?
A) water rushing out of Hoover Dam
B) flashes of light emitted by a firefly
C) a sucrose molecule
D) heat released by a campfire
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best summarizes a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics?
A) If the entropy of a system increases, there must be a corresponding decrease in the entropy of the universe.
B) If the entropy of a system decreases, there must be a corresponding decrease in the entropy of the universe.
C) If entropy of a system decreases, there must be a corresponding increase in the entropy of the universe.
D) Each chemical reaction in an organism must decrease the total entropy of the universe.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics is most likely to be associated with an enzyme that catalyzes two different chemical reactions?
A) The enzyme contains both α-helix and β-pleated sheet regions.
B) The enzyme is subject to both competitive inhibition and allosteric regulation.
C) The enzyme is composed of at least two identical subunits.
D) The enzyme has two distinct active sites.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The 3-D structure of an enzyme composed of a single polypeptide chain includes a large substrate-binding domain. It also has a separate binding site for a regulatory molecule. Based on these structural observations the enzyme is most likely regulated by which of the following mechanism?
A) noncompetitive inhibition
B) competitive activation
C) competitive inhibition
D) cooperativity
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When ATP is hydrolyzed to activate a target protein, what is often the fate of the inorganic phosphate that is released?
A) It is secreted as waste.
B) It is always used to regenerate more ATP.
C) It may be used to form a phosphorylated intermediate.
D) It enters the nucleus to be incorporated in a nucleotide.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes why hydrolysis reactions occur more readily in solution than dehydration reactions do?
A) Hydrolysis reactions increase G, or Gibbs free energy of the system.
B) Hydrolysis reactions are endergonic and increase entropy of the system.
C) Hydrolysis reactions are exergonic and decrease entropy of the system.
D) Hydrolysis reactions are exergonic and increase entropy of the system.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
A) by binding to the active site of the enzyme, thus preventing binding of the normal substrate
B) by binding to an allosteric site, thus changing the shape of the active site of the enzyme
C) by decreasing the free-energy change of the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme
D) by increasing the activation energy of the reaction
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below. 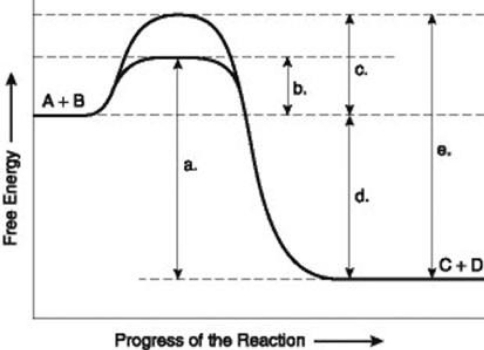 The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the lower-case letters represents the activation energy required for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the lower-case letters represents the activation energy required for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 65
Related Exams