A) The system consumes energy at a steady rate.
B) The system releases energy at a steady rate.
C) The kinetic energy of the system is zero.
D) The system can do no work.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes a common characteristic of catabolic pathways?
A) They combine small molecules into larger, more energy-rich molecules.
B) They require energy from ATP hydrolysis to break down polymers into monomers.
C) They are endergonic and release energy that can be used for cellular work.
D) They are exergonic and provide energy that can be used to produce ATP from ADP and ![]() ᵢ.
ᵢ.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
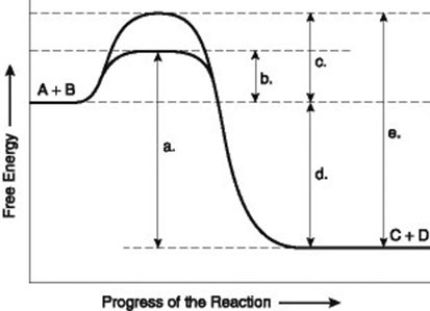 The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure?
The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure?
A) endergonic, ∆G > 0
B) exergonic, ∆G < 0
C) endergonic, ∆G < 0
D) exergonic, ∆G > 0
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When chemical, transport, or mechanical work is done by an organism, what happens to the heat generated?
A) It is used to power yet more cellular work.
B) It is captured to store energy as more ATP.
C) It is used to generate ADP from nucleotide precursors.
D) It is lost to the environment.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a metabolic pathway, succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, a substance that resembles succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase. Increasing the amount of succinate molecules to those of malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid. Which of the following statements correctly describes the role played by molecules described in the reaction?
A) Succinate dehydrogenase is the enzyme, and fumarate is the substrate in the reaction.
B) Succinate dehydrogenase is the enzyme, and malonic acid is the substrate in the reaction.
C) Succinate is the substrate, and fumarate is the product in the reaction.
D) Fumarate is the product, and malonic acid is a noncompetitive inhibitor in the reaction.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
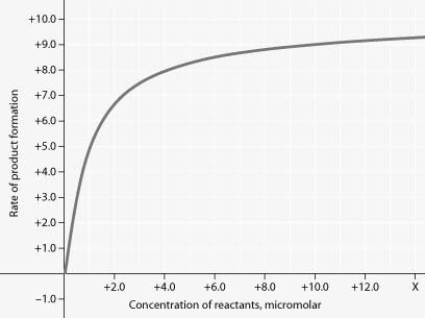 Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant
In the figure, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant
In the figure, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
A) Feedback inhibition by product occurs at high reactant concentrations.
B) Most enzyme molecules are occupied by substrate at high reactant concentrations.
C) The reaction nears equilibrium at high reactant concentrations.
D) The rate of the reverse reaction increases at high reactant concentrations.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is an important consequence of the first law of thermodynamics for a living organism?
A) The energy content of an organism is constant.
B) An organism ultimately must obtain all of the necessary energy for life from its environment.
C) The entropy of an organism decreases with time as the organism grows in complexity.
D) Organisms grow by converting energy into organic matter.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the evolution of life on Earth, from simple prokaryote-like cells to multicellular eukaryotic organisms, is true?
A) By resulting in such diversity and complexity of life, it is an exception to the second law of thermodynamics.
B) It has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics and resulted in a substantial increase in the entropy of the planet.
C) It has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics and resulted in a substantial increase in the total energy in the universe.
D) It has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics and resulted in a substantial decrease in the entropy of the planet.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following metabolic processes can occur without a net influx of energy from some other process?
A) ADP + ![]() → ATP + H₂O
→ ATP + H₂O
B) C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
C) 6CO₂ + 6H₂0 → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
D) Amino acids → Protein
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following conditions may be overcome by increasing the substrate concentration in an enzymatic reaction with a fixed amount of enzyme?
A) the need for a coenzyme
B) allosteric inhibition
C) noncompetitive inhibition
D) competitive inhibition
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most cells cannot harness heat to perform work because
A) heat does not involve a transfer of energy.
B) cells do not have much thermal energy; they are relatively cool.
C) temperature is usually uniform throughout a cell.
D) heat can never be used to do work.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
A) water rushing over Niagara Falls
B) light flashes emitted by a firefly
C) a molecule of glucose
D) a crawling beetle foraging for food
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
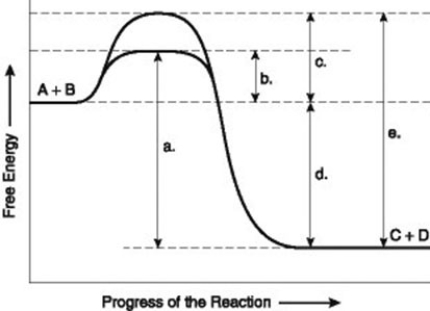 The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following represents the activation energy required for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following represents the activation energy required for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical equilibrium is relatively rare in living cells because metabolic pathways are interconnected. Which of the following statements describes an example of a reaction that may be at chemical equilibrium in a cell?
A) an exergonic reaction in which the free energy at equilibrium is higher than the energy content of the reaction at any point away from equilibrium
B) an exergonic reaction in which the entropy change in the cell is precisely balanced by an opposite entropy change in the cell's surroundings
C) a chemical reaction in which neither the reactants nor the products are being produced or consumed in any metabolic pathway at that time in the cell
D) an endergonic reaction in an active metabolic pathway where the energy for that reaction is supplied only by heat from the environment
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. In the mid-1990s, researchers discovered an enzyme in HIV called protease. Once the enzyme's structure was known, researchers began looking for drugs that would fit into the active site and block it. If this strategy for stopping HIV infections were successful, it would be an example of what phenomenon?
A) noncompetitive inhibition
B) denaturation
C) allosteric regulation
D) competitive inhibition
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chemical reaction that has a positive ΔG is best described as ________.
A) endergonic
B) enthalpic
C) spontaneous
D) exergonic
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as ________ is to ________.
A) exergonic; spontaneous
B) exergonic; endergonic
C) free energy; entropy
D) work; energy
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes the first law of thermodynamics?
A) Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
B) The entropy of the universe is decreasing.
C) The entropy of the universe is constant.
D) Energy cannot be transferred or transformed.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics is most likely to be associated with an enzyme that catalyzes two different chemical reactions?
A) The enzyme contains α-helices and β-pleated sheets.
B) The enzyme is subject to competitive inhibition and allosteric regulation.
C) The enzyme is composed of at least two subunits.
D) Either the enzyme has two distinct active sites or the substrates involved in the two reactions have very similar structures.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a laboratory experiment, you discover that an enzyme-catalyzed reaction has a ∆G of -20 kcal/mol. If you double the amount of enzyme in the reaction, what will be the ∆G for the new reaction?
A) -40 kcal/mol
B) -20 kcal/mol
C) -10 kcal/mol
D) +20 kcal/mol
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 67
Related Exams