A) vesicles
B) breccia
C) porphyritic
D) glassy
E) none of these
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the sites shown in this figure have decompression melting in an oceanic setting? 
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) all of the locations shown
E) locations A and B only
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does the texture of this rock indicate about its cooling history? The magma cooled: 
A) entirely at the surface
B) for a while at some depth and then rose to the surface where it finished solidifying
C) slowly under relatively deep conditions
D) slowly and underwater
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rocks of the continental crust contain different minerals and each mineral has its own melting point. If the minerals with the lowest melting temperatures are the only ones melted, this is referred to as:
A) partial melting
B) complete melting
C) temporary melting
D) subductive melting
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following rock photographs depicts an igneous rock that trapped gas?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following was NOT involved in forming magmas of the main batholith?
A) subduction beneath western North America
B) water that caused partial melting of hot mantle
C) partial melting of continental crust
D) solidification of magma below the surface
E) recent normal faulting along the east side of the batholith
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following rock types does NOT involve dissolved gas in the magma?
A) tuff
B) pumice
C) scoria
D) diorite
E) vesicular basalt
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A volcanic neck can form by:
A) erosion of the volcano, leaving behind the solidified conduit inside the volcano
B) erosion of overlying rock layers exposing the conduit below the volcano
C) both of these
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of heat transfer by convection?
A) water within a pan is heated and flows in a circular path
B) seawater is drawn into a mid-ocean ridge, heated, and rises
C) the rise of material beneath mid-ocean ridges coupled with subduction
D) all of these
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The place in the crust or mantle where igneous rocks begin to form is called the:
A) source area
B) magma chamber
C) intrusive area
D) extrusive area
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Columnar joints, like the ones shown in the photograph, are formed: 
A) when hot but solid igneous rock contracts
B) when hot liquid igneous rock contracts
C) when hot but solid igneous rock expands
D) when hot liquid igneous rock expands
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a way that magma can lose heat to begin solidifying?
A) conduction to surrounding solid rocks
B) loss of thermal energy to the air and water
C) water that is heated and circulated near the magma
D) an increase in the rate of radioactive decay
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are processes that can occur in large magma chambers?
A) Crystals that form may sink or rise in the chamber.
B) A partially crystallized magma could be heated by a new, hotter magma entering the chamber.
C) Magma may partially melt the chamber's rock walls, forming a new magma composition.
D) All of these
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of feldspar and quartz is called:
A) Granite
B) Ryholite
C) Basalt
D) Gabbro
E) Andesite
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mt. Taylor in the diagram has a partial volcanic neck exposed. Which type of volcanic neck is being shown? 
A) beneath a volcano
B) above a volcano
C) with a volcano
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the letters shown on this figure would most likely be over magma related to decompression melting? 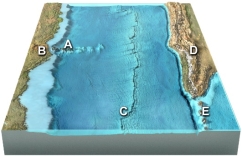
A) A and B
B) A, B, and C
C) B, C, and D
D) C, D, and E
E) D and E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can occur within a magma chamber?
A) Sinking or floating crystals may change the composition of the remaining magma.
B) Wall rocks can melt and become incorporated into the magma.
C) If two magmas mix, the resulting magma would be between the compositions of the two magmas.
D) All of these.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following igneous rocks is NOT characteristic of mid-ocean ridges?
A) finely crystalline rocks that formed in dikes
B) gabbro that solidified in a magma chamber
C) pillow basalt
D) andesite and granodiorite
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does this texture indicate about the formation of this rock? 
A) It formed from an explosive pyroclastic eruption.
B) The rock solidified at great depth.
C) The magma formed some crystals before rising closer to the surface and solidifying.
D) The magma had abundant dissolved gas.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rock that has formed from cooling magma or lava is:
A) Igneous rock
B) Metamorphic rock
C) Sedimentary rock
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 147
Related Exams