A) chloramphenicol.
B) tetracyclines.
C) penicillin G.
D) macrolides.
E) aminoglycosides.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) frequently work by
A) disrupting the plasma membrane.
B) hydrolyzing peptidoglycan.
C) complementary base pairing with DNA.
D) inhibiting cell-wall synthesis.
E) inhibiting protein synthesis.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following antibiotics causes misreading of mRNA?
A) tetracyclines - bind with 30S subunit
B) aminoglycoside - changes shape of 30S units
C) chloramphenicol - inhibits peptide bonds at 50S subunit
D) oxazolidinone - prevents formation of 70S ribosome
E) streptogamin - prevents release of peptide from 70S ribosome
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Interferon inhibits glycolysis.
B) Acyclovir inhibits DNA synthesis.
C) Azoles inhibit plasma membrane synthesis.
D) Amantadine inhibits the release of viral nucleic acid.
E) Fluoroquinolone inhibits DNA synthesis.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Niclosamide prevents ATP generation in mitochondria. You would expect this drug to be effective against
A) helminths.
B) gram-positive bacteria.
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
D) viruses.
E) gram-negative bacteria.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 20.2 The following results were obtained from a disk-diffusion test for microbial susceptibility to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus was the test organism. -In Table 20.2, the most effective antibiotic tested was
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because
A) their cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells.
B) they replicate inside human cells.
C) they do not reproduce.
D) they have more genes than bacteria.
E) they do not have ribosomes.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 20.1 The following data were obtained from a broth dilution test. -In Table 20.1, the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibiotic X is
A) 25 ?g/ml.
B) 15 ?g/ml.
C) 2 ?g/ml.
D) 10 ?g/ml.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 20.1 The following data were obtained from a broth dilution test. -5) In Table 20.1, as illustrated by the data shown, the minimal bactericidal concentration of antibiotic X is
A) 10 ?g/ml.
B) 2 ?g/ml.
C) 25 ?g/ml.
D) 15 ?g/ml.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole inhibit reactions along the same metabolic pathway.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
More than half of our antibiotics are
A) synthesized in laboratories.
B) produced by Fleming.
C) produced by eukaryotic organisms.
D) produced by fungi.
E) produced by bacteria.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following antibiotics is NOT bactericidal?
A) polyenes
B) cephalosporins
C) penicillin
D) aminoglycosides
E) rifampins
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To date, most of our natural antibiotics have been found to be produced by members of what genus?
A) Bacillus
B) Paenibacillus
C) Streptomyces
D) Penicillium
E) Cephalosporium
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 20.2 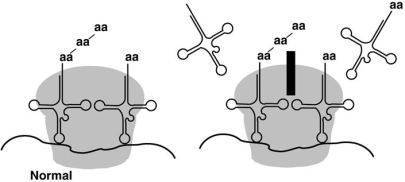 The antibiotic chloramphenicol binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome, as shown in Figure 20.2. The effect is to
The antibiotic chloramphenicol binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome, as shown in Figure 20.2. The effect is to
A) prevent peptide bond formation in prokaryotes.
B) prevent transcription in prokaryotes.
C) prevent polypeptide elongation in eukaryotes.
D) prevent ribosome formation in bacteria.
E) prevent mRNA-ribosome binding in eukaryotes.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about drugs that competitively inhibit DNA polymerase or RNA polymerase is FALSE?
A) They are used against viral infections.
B) They cause cellular plasmolysis.
C) They can affect host cell DNA synthesis.
D) They interfere with protein synthesis.
E) They can potentially cause mutations.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 55 of 55
Related Exams