A) sleep movements.
B) tropisms.
C) physiological requirements.
D) circadian rhythms.
E) biological clocks.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plant growth and development is guided by
A) hormones.
B) other signaling molecules.
C) water availability.
D) day length.
E) all of these.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the above figure to answer questions
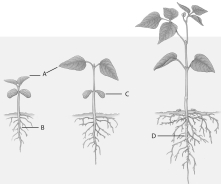 -The letter "A" in the above figure represents
-The letter "A" in the above figure represents
A) the root nodules.
B) the primary root.
C) the primary leaf.
D) the cotyledons.
E) none of these.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemicals produced by one group of cells that affect other target cells are called
A) secretions.
B) signaling molecules.
C) steroids.
D) polymers.
E) enzymes.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Auxin concentration gradients
A) appear once germination begins.
B) cause regional differences in gene transcription.
C) allow formation of plant parts in expected patterns.
D) help young cells elongate so that shoots and roots lengthen.
E) are described by all EXCEPT "appear once germination begins."
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure above to answer questions
 -The function of "A" is to
-The function of "A" is to
A) digest the endosperm.
B) protect new leaves as the seedling grows through soil.
C) secrete hormones that cause flowering.
D) absorb pheromones secreted by other seedlings.
E) do none of these.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
2,4-D, a potent eudicot weed killer, is most likely a synthetic
A) auxin.
B) gibberellin.
C) cytokinin.
D) phytochrome.
E) none of these.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Growth refers to an increase in the __________ of cells.
A) size
B) number
C) differentiation
D) volume
E) all EXCEPT "differentiation"
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What hormone(s) can be used commercially to prolong the shelf life of cut flowers?
A) abscisic acid
B) cytokinins
C) auxins
D) ABA
E) ethylene
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the above figure to answer questions
 -The letter "B" in the above figure represents
-The letter "B" in the above figure represents
A) the root nodules.
B) the primary root.
C) the primary leaf.
D) the cotyledons.
E) none of these.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The plant hormone that promotes cell division in roots and shoots is
A) auxin.
B) gibberellin.
C) cytokinin.
D) abscisic acid.
E) ethylene.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All EXCEPT which of the following has an effect on seed germination?
A) moisture
B) temperature
C) carbon dioxide
D) number of daylight hours
E) oxygen
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which factor has NOT been implicated in breaking dormancy?
A) cytokinin movement from leaves to buds in late summer
B) action of abscisic acid in the spring
C) gibberellin accumulation in buds in late autumn and winter
D) an exposure to low temperatures for hundreds of hours
E) all of these
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the above figure to answer questions
 -The letter "C" in the above figure represents
-The letter "C" in the above figure represents
A) the root nodules.
B) the primary root.
C) the primary leaf.
D) the cotyledons.
E) none of these.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is false regarding plant hormones?
A) They are signaling molecules that travel to target cells.
B) They stimulate or inhibit gene activity.
C) They bind to receptors on their target cells.
D) Target cells are always adjacent to the secreting cell.
E) All of these are false.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aging of a plant is
A) senescence.
B) vernalization.
C) abscission.
D) dormancy.
E) chlorosis.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the above figure to answer questions
 -The letter "D" in the above figure represents
-The letter "D" in the above figure represents
A) the root nodules.
B) the primary root.
C) the primary leaf.
D) the cotyledons.
E) none of these.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared with young trees growing out in the open, young trees growing in a darker forest understory tend to have longer, thinner trunks with less branching.This developmental pattern is principally caused by
A) phototropism.
B) thigmotropism.
C) activated phytochrome being converted to inactive phytochrome.
D) inactive phytochrome being converted to active phytochrome.
E) none of these.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The plant movement in the above figure is caused by
A) auxin differences in two sides of the coleoptile.
B) gibberellin released in one side of the leaf.
C) abscisic acid in two sides of the stems.
D) salicylic acid in two sides of the roots.
E) none of these.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary root of a seedling grows down
A) to avoid light.
B) in response to gravity.
C) because the cells on the upper surface of the root elongate more rapidly than those on the lower surface of the root.
D) in response to different concentrations of auxin.
E) because of all of these except "to avoid light."
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 77
Related Exams