A) Enzyme function is generally increased if the three-dimensional structure or conformation of an enzyme is altered.
B) Enzyme function is independent of physical and chemical environmental factors such as pH and temperature.
C) Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers.
D) Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions by providing activation energy to the substrate.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true for a system at chemical equilibrium?
A) The system consumes energy at a steady rate.
B) The system releases energy at a steady rate.
C) The kinetic energy of the system is zero.
D) The system can do no work.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical equilibrium is relatively rare in living cells because metabolic pathways are interconnected. Which of the following statements describes an example of a reaction that may be at chemical equilibrium in a cell?
A) an exergonic reaction in which the free energy at equilibrium is higher than the energy content of the reaction at any point away from equilibrium
B) an exergonic reaction in which the entropy change in the cell is precisely balanced by an opposite entropy change in the cell's surroundings
C) a chemical reaction in which neither the reactants nor the products are being produced or consumed in any metabolic pathway at that time in the cell
D) an endergonic reaction in an active metabolic pathway where the energy for that reaction is supplied only by heat from the environment
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A series of enzymes catalyze the reactions in the metabolic pathway X → Y → Z → A. Product A binds to the enzyme that converts X to Y at a position remote from its active site. This binding decreases the activity of the enzyme. With respect to the enzyme that converts X to Y, substance A functions as ________.
A) an allosteric inhibitor
B) the substrate
C) an intermediate
D) a competitive inhibitor
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A number of systems for pumping ions across membranes are powered by ATP. Such ATP-powered pumps are often called ATPases, although they do not often hydrolyze ATP unless they are simultaneously transporting ions. Because small increases in calcium ions in the cytosol can trigger a number of different intracellular reactions, cells keep the cytosolic calcium concentration quite low under normal conditions, using ATP-powered calcium pumps. For example, muscle cells transport calcium from the cytosol into the membranous system called the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) . If a resting muscle cell's cytosol has a free calcium ion concentration of 10⁻⁷ while the concentration in the SR is 10⁻², then how is the ATPase acting?
A) ATPase activity must be powering an inflow of calcium from the outside of the cell into the SR.
B) ATPase activity must be transferring ![]() ᵢ to the SR to enable this to occur.
ᵢ to the SR to enable this to occur.
C) ATPase activity must be pumping calcium from the cytosol to the SR against the concentration gradient.
D) ATPase activity must be opening a channel for the calcium ions to diffuse back into the SR along the concentration gradient.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following graphs most likely describes the effect of pH on the function of the enzyme catalase in human cells? Note: The x-axis is pH and the y-axis is enzyme activity.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How might a change of one amino acid at a site, distant from the active site of an enzyme, alter the substrate specificity of an enzyme?
A) by changing the stability of the enzyme
B) by changing the three-dimensional conformation of the enzyme
C) by changing the optimum pH for the enzyme
D) by changing the binding site for a noncompetitive inhibitor
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A series of enzymes catalyze the reactions in the metabolic pathway X → Y → Z → A. Product A binds to the enzyme that converts X to Y at a position remote from its active site. This binding decreases the activity of the enzyme. What is substance X?
A) an allosteric inhibitor
B) a substrate
C) an intermediate
D) the product
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
A) water rushing over Niagara Falls
B) light flashes emitted by a firefly
C) a molecule of glucose
D) a crawling beetle foraging for food
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a metabolic pathway, succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, a substance that resembles succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase. Increasing the amount of succinate molecules to those of malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid. What role does malonic acid play with respect to succinate dehydrogenase?
A) Malonic acid is a competitive inhibitor.
B) Malonic acid blocks the binding of fumarate.
C) Malonic acid is a noncompetitive inhibitor.
D) Malonic acid is an allosteric regulator.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following aspects of enzyme structure is best described by a clasping handshake analogy?
A) the specific manner in which an enzyme folds to form secondary and tertiary structures
B) the specific manner in which an enzyme interacts with water
C) the specific manner in which an enzyme binds substrate
D) the specific manner in which an enzyme is denatured by low pH
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
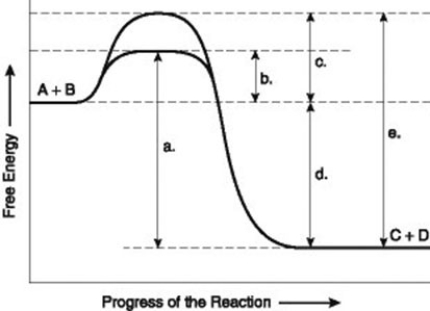 The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following represents the activation energy required for the non-enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following represents the activation energy required for the non-enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. In the mid-1990s, researchers discovered an enzyme in HIV called protease. Once the enzyme's structure was known, researchers began looking for drugs that would fit into the active site and block it. If this strategy for stopping HIV infections were successful, it would be an example of what phenomenon?
A) noncompetitive inhibition
B) denaturation
C) allosteric regulation
D) competitive inhibition
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in entropy is associated with which type of reaction?
A) dehydration
B) catabolic
C) depolymerization
D) hydrolysis
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes a common characteristic of catabolic pathways?
A) They combine small molecules into larger, more energy-rich molecules.
B) They require energy from ATP hydrolysis to break down polymers into monomers.
C) They are endergonic and release energy that can be used for cellular work.
D) They are exergonic and provide energy that can be used to produce ATP from ADP and ![]() ᵢ.
ᵢ.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do hydrolysis reactions occur more readily in solution than dehydration reactions?
A) Hydrolysis reactions increase G, or Gibbs free energy of the system.
B) Hydrolysis reactions are endergonic and increase entropy of the system.
C) Hydrolysis reactions are exergonic and decrease entropy of the system.
D) Hydrolysis reactions are exergonic and increase entropy of the system.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about anabolic pathways is true?
A) They are usually spontaneous chemical reactions.
B) They consume energy to build up polymers from monomers.
C) They release energy by degrading polymers to monomers.
D) They decrease the entropy of the organism and its environment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ is a regulatory mechanism in which the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme that catalyzes an early step in the pathway.
A) Allosteric inhibition
B) Cooperative inhibition
C) Feedback inhibition
D) Metabolic inhibition
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
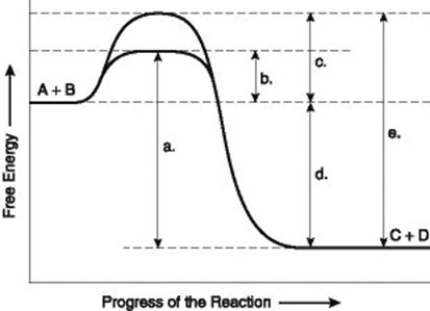 The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure?
The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure?
A) endergonic, ∆G > 0
B) exergonic, ∆G < 0
C) endergonic, ∆G < 0
D) exergonic, ∆G > 0
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When ATP releases some energy, it also releases inorganic phosphate. What happens to the inorganic phosphate in the cell?
A) It is secreted as waste.
B) It is used only to regenerate more ATP.
C) It may be used to form a phosphorylated intermediate.
D) It enters the nucleus to be incorporated in a nucleotide.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 67
Related Exams