A) Periosteum
B) Sharpey fibers
C) Growth plate
D) Medullary cavity
E) Endosteum
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
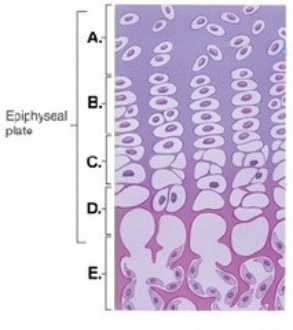 -This figure illustrates bone growth in length at the epiphyseal plate. Zone "C" represents
-This figure illustrates bone growth in length at the epiphyseal plate. Zone "C" represents
A) bone tissue of the diaphysis.
B) zone of calcification.
C) zone of hypertrophy.
D) zone of proliferation.
E) zone of resting cartilage.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In appositional growth of cartilage,
A) chondroblasts within the tissue proliferate and add more matrix from the inside.
B) new chondrocytes and new matrix are added on the outside of the tissue.
C) osteoblasts replace the chondroblasts.
D) the tissue becomes vascularized in order to grow.
E) the cartilage is replaced with another kind of connective tissue.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do the lymphatic and immune systems contribute to osteoporosis?
A) Macrophages in the skin destroy the precursor to vitamin D.
B) Immune cells resist infections and release chemicals that promote tissue repair.
C) Excessive smoking stimulate immune cells to attack bones, which increases bone loss.
D) Calcium ions are excreted by immune cells at the lymph nodes.
E) Decreased estrogen levels following a viral infection contribute to the disease.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) causes
A) increased RANKL and increased OPG.
B) increased RANKL and decreased OPG.
C) decreased RANKL and increased OPG.
D) decreased RANKL and decreased OPG.
E) PTH has no effect on RANKL and OPG.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The covering of the outer surface of bone is the ________.
A) lamellae
B) lacunae
C) canaliculi
D) periosteum
E) trabeculae
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which type of bonet tissue are osteons present?
A) Spongy bone
B) Compact bone
C) Both "spongy bone" and "compact bone" are correct.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Normal bone growth requires adequate amounts of certain substance from the diet. Which of the following list three of the dietary needs for normal bone growth?
A) Sodium, calcium, and vitamin E
B) Potassium, calcium, and vitamin D
C) Calcium, phosphate, and vitamin D
D) Vitamin D, phosphate, and chloride
E) Vitamin E, vitamin B, and vitamin A
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The zygomatic bone is an example of a(n) ________ bone.
A) long
B) flat
C) short
D) irregular
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A band of connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone is a/an ________.
A) aponeurosis
B) ligament
C) bursa
D) epimysium
E) tendon
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about bone remodeling and repair is correct?
A) Bone remodeling involves removal of old bone by osteoblasts.
B) As a long bone increases in diameter, the size of the marrow cavity decreases.
C) The rate of bone remodeling increases in the elderly.
D) Exposure of a bone to increased mechanical stress can lead to bone remodeling.
E) Bone remodeling does not involve the activity of the osteoclasts and the osteoblasts.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Small channels extending through the bone matrix are ________.
A) lamellae
B) lacunae
C) canaliculi
D) periosteum
E) trabeculae
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cell type that is responsible for maintaining bone once it has been formed is the ________.
A) osteoclast
B) osteoblast
C) chondrocyte
D) osteocyte
E) chondroblast
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
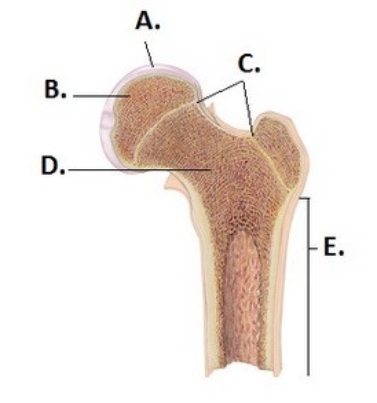 -What does structure "D" represent on the bone diagram?
-What does structure "D" represent on the bone diagram?
A) Spongy bone
B) Diaphysis
C) Epiphyseal lines
D) Articular cartilage
E) Epiphysis
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A) Osteocyte - functions in bone remodeling
B) Osteoclast - responsible for reabsorption
C) Osteoblast - breaks down bone tissue
D) Endosteum - lines central canal of the osteon
E) Periosteum - lines the medullary cavity
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The remodeling of bone tissue is a function of
A) osteoblast and osteoclast activity.
B) osteoclast and osteocyte activity.
C) chondroblast and osteoclast activity.
D) chondrocyte and osteocyte activity.
E) fibroblast and chondroblast activity.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long bones grow in length at the ________.
A) epiphyseal plate
B) articular cartilage
C) center of the shaft
D) endosteum-periosteum junction
E) center of the epiphysis
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some flat and irregular bones of the skull have air-filled spaces called ________.
A) epiphyseal spaces
B) medullary cavities
C) lacunae
D) sinuses
E) trabeculae
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of bone cell incorporates calcium and phosphate ions into bone tissue?
A) Osteochondral progenitor cell
B) Osteoblast
C) Osteocyte
D) Osteoclast
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a direct effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) ?
A) Increased Ca2+ uptake by the small intestine
B) Increased vitamin D formation in the kidneys
C) Increased Ca2+ reabsorption by the kidneys
D) Decreased Ca2+ loss by the kidneys
E) All of the choices are direct effects of PTH.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 178
Related Exams