A) Repetitive stress on the long bones will solidify cartilage.
B) The Haversian canal system will supply more blood and strengthen the bone.
C) The repetitive stress will lead to remodeling and strengthening of the long bones.
D) The marrow cavity will solidify and strengthen the bone.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for an earthworm to lengthen several contiguous segments of its body, it must
A) contract its longitudinal muscles, which pulls up the chaetae and moves the body fluid perpendicular to the long axis of the worm.
B) contract its longitudinal muscles, which extends the chaetae into the surrounding soil and moves the body fluid parallel to the long axis of the worm.
C) contract its circular muscles, which extends the chaetae into the surrounding soil and moves the body fluid parallel to the long axis of the worm.
D) contract its circular muscles, which pulls up the chaetae and moves the body fluid parallel to the long axis of the worm.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In arthropods, locomotion is accomplished by muscles that work against
A) each other.
B) the exoskeleton.
C) a hydrostatic skeleton.
D) mineralized bones.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the Baby Boomer generation ages, more and more joint replacement surgeries take place each year.Hip replacement surgery is the gold standard of all joint replacement surgeries, with many patients able to walk just a few hours after surgery and return home the very next day.In contrast, knee replacement surgery usually requires hospital stays of several days, followed by weeks to months of physical therapy.What best explains why the recovery after hip replacement surgery is so much faster than after knee replacement surgery?
A) The hip joint is more superficial and more accessible to surgeons than the knee joint.
B) The hip only moves in one direction, and recovery of one motion is easier than recovering movement in many directions.
C) The upper end of the thigh bone has less overall surface contact with the hip bone than its lower end has in the knee with bones of the lower leg.
D) The knee joint is stabilized by many more structures (many of which have to be cut) than the hip joint.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The myofibrils consist of both thin filaments made of actin and thick filaments composed of
A) tropomyosin.
B) myosin.
C) acetylcholine.
D) troponin.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The neurotransmitter released from the nerve terminus at the neuromuscular junction is __________.
A) troponin
B) Ca2+
C) tropomyosin
D) acetylcholine
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sarin gas is an inhibitor of an enzyme that functions in the neuromuscular junction to break down acetylcholine.What is the most likely description of how a person would die after inhaling this poisonous gas?
A) suffocation via paralysis, or a block in stimulation, of the respiratory muscles
B) epileptic convulsions caused by disorganized electrical activity in the brain
C) by a heart attack
D) suffocation via tetanus, or constant stimulation, of the respiratory muscles
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The muscles that move the eye have a high proportion of fast-twitch fibers and reach maximum tension very fast.These fibers belong to the class of __________ fibers.
A) type I
B) type II
C) type III
D) type IV
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a stimulated muscle fiber, the calcium ions released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum bind to the protein _______.
A) myosin
B) tropomyosin
C) actin
D) troponin
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these muscles would you expect to have the greatest proportion of slow-twitch fibers?
A) the lateral rectus
B) chicken breast muscle
C) the soleus
D) the gastrocnemius
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you rub the scaled skin of a shark, it feels rough if you move your hand from tail to head but smooth if you move from head to tail.What is a major advantage of the scales being oriented this way?
A) to keep the shark afloat in the water
B) to counteract friction as the shark swims through the water
C) to better protect the shark from predators
D) to better prevent water loss from the body tissues
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are investigating the scene of a hit and run where somebody's pet dog was killed.It is a very hot day so the dog's body temperature is unlikely to yield any important information regarding the time of death.The dog's limbs are movable and there is no significant smell of rotting flesh.What is the best guess of the time of death?
A) within the last 10 minutes
B) within the last 2 hours
C) 3-4 hours ago
D) 24 hours ago
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the incorrect statement related to sarcomere structure and function.
A) Two Z lines form the opposite borders of one sarcomere.
B) Thin filaments are not present in the H band of a sarcomere.
C) I bands consist of both thin and thick filaments.
D) Stacks of thick filaments produce dark bands, called the A band.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mammalian jaw is an example of what kind of moveable joint?
A) gliding joint
B) ball-and-socket joint
C) hinge joint
D) combination joint
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vertebrate bone does NOT ____.
A) contain blood vessels
B) contain sarcomere units
C) contain hydroxyapatite crystals
D) become remodeled with use
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have just read an advertisement for a new drug that claims people who take it can get muscular bodies without spending months lifting weights in the gym.The drug stimulates muscle growth in the same way that weight lifting does, which is to
A) stimulate existing muscle fibers to divide.
B) stimulate growth in the size of existing muscle fibers.
C) stimulate an increase in the proportion of slow-twitch muscle fibers.
D) stimulate existing muscle fibers to fuse with one another.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the power stroke shown in panel c below, the thin filaments are pulled towards the center of the sarcomere.What is the specific sequence of events that occurs during a power stroke? 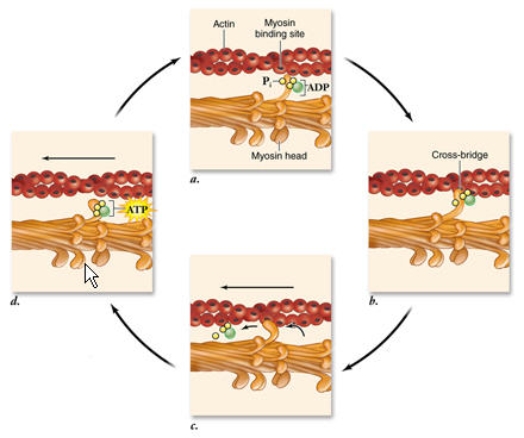
A) Release of the phosphate group -> release of ADP -> myosin head changes shape
B) Release of ADP-> release of the phosphate group -> myosin head changes shape
C) Release of ADP -> myosin head changes shape -> release of the phosphate group
D) Release of the phosphate group -> myosin head changes shape -> release of ADP
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the association between tropomyosin and troponin molecules in resting striated muscle fibers?
A) Tropomyosin holds the troponin in place on the myosin.
B) Troponin holds the tropomyosin in place on the myosin.
C) Tropomyosin holds the troponin in place on the actin.
D) Troponin holds the tropomyosin in place on the actin.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The movement of actin and myosin fibers in a muscle contraction contains all of the following steps EXCEPT
A) the myosin head attaches to the actin filament.
B) the globular myosin head detaches from the actin filament.
C) myosin rolls up from one end, forming a ball.
D) the myosin head returns to its original conformation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What molecule contributes to the red color of slow-twitch muscle fibers?
A) myoglobin
B) ATP
C) glycogen
D) lactic acid
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 45
Related Exams