A) starch
B) cellulose
C) lactose
D) sucrose
E) glucose
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which enantiomer of glyceraldehyde is represented in the following structure? 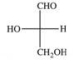
A) trans
B) α
C) β
D) D
E) L
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What polysaccharide found in animals has a structure very similar to amylopectin?
A) glucose
B) glycogen
C) starch
D) amylose
E) cellulose
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monosaccharide derivative shown below bonds to hydrophobic molecules in the liver.What effect does this have on the molecule to which it binds? 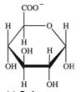
A) It increases the hydrophobicity of the molecule, making it more soluble in fatty tissues.
B) It increases the polarity of the molecule, making it more soluble in bodily fluids, and more readily removed.
C) It eliminates the ability of the molecule to act as a nutritional source of energy.
D) It decreases the polarity of the hydrophobic molecule, allowing it to be retained in the body longer.
E) It increases the nutritional value of the molecule by allowing it to be retained by the body longer.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning stereochemistry is INCORRECT?
A) Stereoisomers are molecules with the same molecular formula, same bonding pattern, but different spatial arrangement of atoms.
B) A chiral carbon is a carbon atom that has four different groups bonded to it.
C) A molecule that contains a chiral carbon is a chiral molecule, and exists as a pair of enantiomers.
D) Enantiomers are superimposable mirror image stereoisomers.
E) A racemic mixture of enantiomers is optically inactive.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of product forms in the intramolecular reaction between the aldehyde portion of the glucose molecule below and its C-5 hydroxyl group? 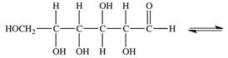
A) disaccharide
B) ester
C) carboxylic acid
D) stereoisomer
E) hemiacetal
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Fischer projections of two monosaccharides are shown below.What is the relationship between the two monosaccharides? 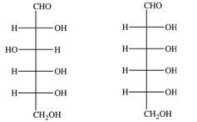
A) enantiomers
B) diastereomers
C) structural isomers
D) meso isomers
E) cis-trans isomers
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What two monosaccharides combine to form sucrose?
A) glucose and galactose
B) galactose and fructose
C) ribose and galactose
D) glucose and fructose
E) ribose and fructose
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of compound is produced in the reaction between an alcohol and an aldehyde?
A) diol
B) carboxylic acid
C) acetal
D) hemiacetal
E) ester
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Melibiose is a carbohydrate found in some plant juices.Which of the following statements concerning melibiose is INCORRECT? 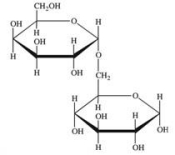
A) It is a disaccharide.
B) It is composed of two different monosaccharide units.
C) It contains both an acetal and a hemiacetal.
D) It contains an α(1→5) glycosidic linkage.
E) It is a reducing sugar.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What test can be used to distinguish between a reducing sugar and a nonreducing sugar?
A) iodine test
B) Tollens' test
C) chromic acid test
D) Benedict's test
E) hydrolysis test
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What term describes a carbon atom that has four different groups bonded to it?
A) chiral
B) unbalanced
C) trigonal pyramidal
D) meso
E) unsaturated
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If D-glucose is levorotatory, then L-glucose must be levorotatory as well.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Propranol is a chiral compound that exists as a pair of enantiomers.One enantiomer is used to treat irregular heartbeats, and the other is used as a contraceptive.Which labeled carbon atom(s) is/are chiral? 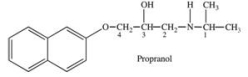
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-3
D) C-4
E) C-1 and C-3
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do the structures of amylose and cellulose differ?
A) Amylose is a linear polysaccharide and cellulose is a branched polysaccharide.
B) Amylose is a homopolysaccharide and cellulose is a heteropolysaccharide.
C) Amylose is a polysaccharide of glucose units, and cellulose is a polysaccharide of galactose units.
D) Amylose is a polysaccharide made up of D-glucose units, and cellulose is a polysaccharide made up of L-glucose units.
E) Amylose contains α(1→4) glycosidic bonds joining D-glucose units, and cellulose contains β(1→4) glycosidic bonds joining D-glucose units.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a carbohydrate?
A) sucrose
B) simple sugar
C) fatty acid
D) cellulose
E) starch
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starch is composed of which two polysaccharides?
A) chitin and chondroitin
B) glycogen and cellulose
C) amylose and amylopectin
D) glucosamine and glycogen
E) cellulose and galactosamine
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which carbohydrate is present in RNA?
A) ribulose
B) glucose
C) mannose
D) ribose
E) fructose
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cellulose molecules are all unbranched, while starch contains only branched molecules.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
All monosaccharides give a positive result with Benedict's reagent.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 74
Related Exams