B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a regressive tax system, as the level of income increases in an economy, the average tax rate will:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain constant.
D) either increase or decrease.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
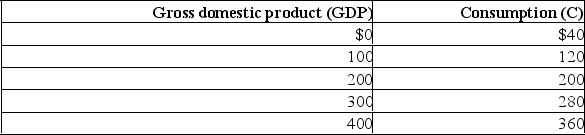 Refer to the above data.If a lump-sum tax (the same tax amount at each level of GDP) of $40 is imposed in this economy, the tax system:
Refer to the above data.If a lump-sum tax (the same tax amount at each level of GDP) of $40 is imposed in this economy, the tax system:
A) is regressive.
B) is proportional.
C) is progressive.
D) may be either proportional or progressive.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The actual and full-employment budgets will be equal when the economy is at full-employment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an economy, the government wants to increase aggregate demand by $48 billion at each price level to increase real GDP and reduce unemployment.If the MPC is .75, then it could:
A) reduce taxes by $12 billion.
B) reduce taxes by $16 billion.
C) reduce government spending by $12 billion.
D) increase government spending by $18 billion.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using Image 13.2 Global Perspective, which of the following countries had the lowest public debt as a percentage of GDP in 2015?
A) France
B) Belgium
C) Spain
D) Canada
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economy is experiencing a high rate of inflation.The government wants to reduce GDP by $36 billion to reduce inflationary pressure.The MPC is .75.By how much should the government raise taxes to achieve its objective?
A) $6 billion
B) $9 billion
C) $12 billion
D) $16 billion
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A contractionary fiscal policy shifts the aggregate demand curve leftward and may or may not reduce real GDP.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "cyclically adjusted budget" refers to:
A) the inflationary impact which the automatic stabilizers have in a full-employment economy.
B) that portion of a full-employment GDP which is not consumed in the year it is produced.
C) the size of the federal government's budgetary surplus or deficit when the economy is operating at full employment.
D) the number of workers who are underemployed when the level of unemployment is 7 to 8 percent.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the full-employment budget surplus as a percentage of GDP over a five-year period.  Refer to the above information.In which year was fiscal policy contractionary?
Refer to the above information.In which year was fiscal policy contractionary?
A) Year 2
B) Year 3
C) Year 4
D) Year 5
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the timing problems with fiscal policy is an "operational lag" that occurs between the:
A) beginning of a recession and the time that it is recognized that the event is occurring.
B) time the need for fiscal action is recognized and the time that action is actually taken.
C) time that fiscal action is taken and the time that action has an impact on output, employment, and the price level.
D) time that fiscal action has an impact on output, employment, and the price level and the time by which it can be determined if the policy is effective.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Built-in stability only partially offsets fluctuations in economic activity.
B) Built-in stability works in halting inflation, but it cannot alleviate unemployment.
C) Built-in stability can be relied on to eliminate completely any fluctuation in economic activity.
D) Built-in stability overcorrects for fluctuations in economic activity; for example, it may change a small expansion into a recession.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the graph given below. 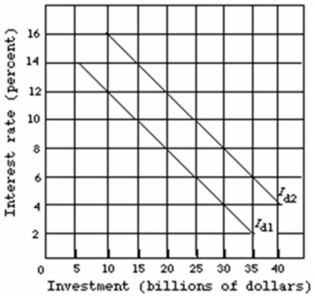 Assume that the investment demand curve of an economy is Id1 in period 1.The crowding-out effect of a large government deficit would be shown as a(n) :
Assume that the investment demand curve of an economy is Id1 in period 1.The crowding-out effect of a large government deficit would be shown as a(n) :
A) shift of the investment demand curve from Id1 to Id2.
B) leftward shift of the investment demand curve.
C) increase in the interest rate from 4 percent to 6 percent and a decline in investment spending of $5 billion.
D) increase in the interest rate from 6 percent to 8 percent and a decline in investment spending of $40 billion.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An appropriate fiscal policy for severe demand-pull inflation is:
A) an increase in government spending.
B) depreciation of the dollar.
C) a reduction in interest rates.
D) a tax rate increase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A public debt which is owed to foreigners can be burdensome because:
A) foreign interest rates are persistently higher than domestic interest rates.
B) payment of interest reduces the volume of goods and services available for domestic uses.
C) payment of interest will conflict with a nation's foreign aid programs.
D) payment of interest will necessarily have a deflationary effect on prices in the paying nation.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The financing of a government deficit increases interest rates and, as a result, reduces investment spending.This statement describes:
A) the supply-side effects of fiscal policy.
B) built-in stability.
C) the crowding-out effect.
D) the net export effect.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Within the aggregate demand and aggregate supply framework, fiscal policy that emphasizes activist government policies to stabilize the economy would view cutting personal income taxes as primarily a shift:
A) right in the aggregate demand curve.
B) left in the aggregate demand curve.
C) right in the aggregate supply curve.
D) left in the aggregate supply curve.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The federal budget deficit is found by:
A) subtracting government tax revenues plus government borrowing from government spending in a particular year.
B) subtracting government tax revenues from government spending in a particular year.
C) cumulating the differences between government spending and tax revenues over all years since the nation's founding.
D) subtracting government revenues from the non-investment-type government spending in a particular year.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in an economy with an MPC of .8 the government wanted to shift the aggregate demand curve leftward by $40 billion at each price level to remedy demand-pull inflation.It could:
A) increase taxes by $10 billion.
B) reduce government spending by $40 billion.
C) reduce government spending by $5 billion.
D) increase taxes by $20 billion.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
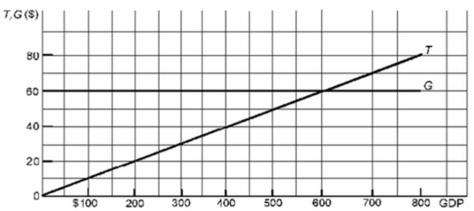 Refer to the above diagram where T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures.All figures are in billions of dollars.If the full-employment and actual GDP are each $400 billion, government can balance its budget by:
Refer to the above diagram where T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures.All figures are in billions of dollars.If the full-employment and actual GDP are each $400 billion, government can balance its budget by:
A) increasing T by $40 billion.
B) reducing G by $20 billion.
C) reducing T by $20 billion.
D) increasing T by $10 billion and reducing G by $20 billion.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 234
Related Exams