A) because the rate of inflation is steady in the long run.
B) Input prices eventually rise in response to changes in output prices.
C) because product prices always increase at a faster rate than resource prices.
D) only when the money supply increases at the same rate as real GDP.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
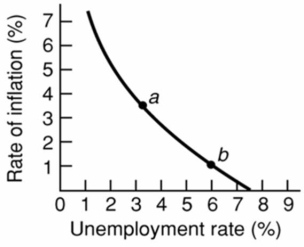 Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Which of the following best describes the relationship shown by this curve?
Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Which of the following best describes the relationship shown by this curve?
A) The demand for labor is large when the rate of inflation is small.
B) When the rate of unemployment is high, the rate of inflation is high.
C) The rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment are inversely related.
D) The rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment are directly related.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Phillips Curve is based on the idea that with a constant short-run aggregate supply curve, a greater increase in aggregate demand is associated with a:
A) smaller increase in price level.
B) smaller increase in nominal wage rates.
C) greater increase in the unemployment rate.
D) greater increase in the rate of inflation.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using Image 16.1 Global Perspective, which of the following countries had the lowest misery index in 2014?
A) United Kingdom
B) France
C) Canada
D) United States
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A criticism of the arguments for tax cuts made by supply-side economists is that the:
A) demand-side effects will be stronger than the supply-side effects.
B) supply-side effects will be stronger than the demand-side effects.
C) supply-side effects will increase saving and reduce consumption.
D) demand-side effects will reinforce the supply-side effects, thus creating cost-push inflation.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
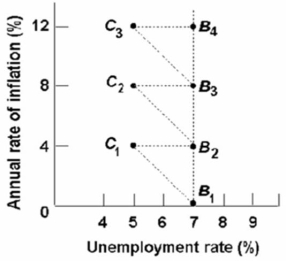 Refer to the above graph.The full-employment unemployment rate in this economy would be:
Refer to the above graph.The full-employment unemployment rate in this economy would be:
A) 5 percent.
B) 6 percent.
C) 7 percent.
D) 5-6 percent.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run aggregate supply curve:
A) is downward sloping.
B) is vertical.
C) is horizontal.
D) is upward sloping.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long-run equilibrium occurs where:
A) real output is greater than potential output.
B) the vertical long-run aggregate supply curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve intersect.
C) the aggregate demand curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve intersect
D) the aggregate demand curve, vertical long-run aggregate supply curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve all intersect.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the graph below.Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AS1 intersects AD1.Then a supply shock occurs that shifts AS1 to AS2.If the government counters with an expansionary fiscal policy that shifts AD1 to AD2, then it is most likely that: 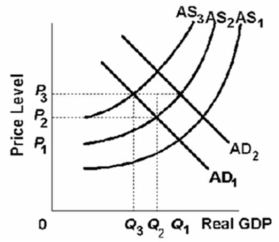
A) AD2 will shift to AD1.
B) AS2 will shift to AS1.
C) AS2 will shift to AS3.
D) AS2 will shift to AS3 and AD2 will shift to AD1.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As real GDP increases the equilibrium point of aggregate demand (AD) and short run aggregate (SRAS) supply move how, with regards to long run aggregate (LRAGS) supply?
A) The LRAGS moves to the right, and the AD and SRAS move up.
B) The LRAGS moves to the right, and the AD and SRAS move down.
C) The LRAGS moves to the left, and the AD and SRAS move up.
D) The LRAGS moves to the left, and the AD and SRAS move down.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal, a decrease in the price level will:
A) shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C) cause a movement up a short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) cause a movement down a short run aggregate supply curve.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
More inflation is likely to result when the government enacts policies to maintain full employment when there is cost-push inflation.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which factor contributed to the termination of stagflation in the 1980s?
A) less foreign competition
B) more government regulation
C) a reduction in oil prices
D) a rise in per-unit production costs
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Based on the long-run Phillips Curve, any particular rate of inflation is compatible in the long run with the natural rate of unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long-run, any inflation that occurs in the economy is the result of:
A) the reduction in the rate of increase in money supply.
B) the growth of aggregate supply.
C) the growth of aggregate demand.
D) the growth of real GDP.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic growth driven by supply factors causes:
A) continuous leftward shifts of aggregate supply.
B) a rightward shift of an economy's long-run aggregate supply.
C) one time shift in aggregate supply.
D) no shift in aggregate supply.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One policy dilemma posed by cost-push inflation is that:
A) an increase in aggregate demand will increase inflation and the unemployment rate simultaneously.
B) tax rates can be reduced without lowering tax revenues.
C) the reduction of aggregate demand to restrain inflation will cause a further reduction in the real GDP.
D) the adjustment of aggregate demand can neither increase real GDP nor reduce inflation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
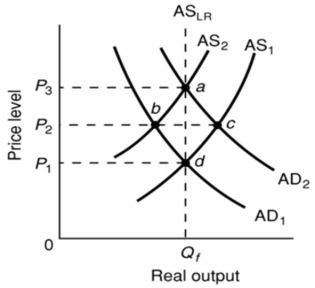 Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.In the long run, demand-pull inflation is best shown as:
Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.In the long run, demand-pull inflation is best shown as:
A) a shift of aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 followed by a shift of aggregate supply from AS1 to AS2.
B) a move from d to b to a.
C) a shift of aggregate supply from AS1 to AS2 followed by a shift of aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2.
D) a move from a to d.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
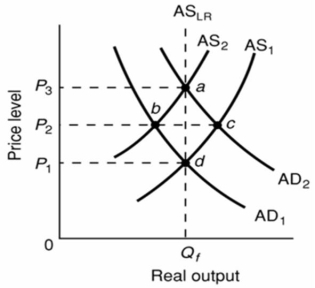 The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.In the long run, the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the diagram because:
The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.In the long run, the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the diagram because:
A) nominal wages and other input prices are assumed to be fixed.
B) real output level Qf is the potential level of output.
C) price level increases produce perfectly offsetting changes in nominal wages and other input prices.
D) higher than expected rates of actual inflation reduce real output only temporarily.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the short run, demand-pull inflation will drive up the price level and increase real output; in the long run, only the price level will rise.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 122
Related Exams