A) governments at all levels coordinating the activities of firms and citizens.
B) individuals forming cooperative enterprises and labour unions.
C) individuals following their own self interest, doing what seems best for themselves.
D) benevolent individuals pursuing the public interest.
E) the self-interested behaviour of a small number of individuals.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a diagram of a production possibilities boundary, the concept of scarcity is illustrated by the
A) points on the boundary.
B) area within the boundary.
C) distance from the origin to the boundary.
D) negative slope of the boundary.
E) unattainable points outside the boundary.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-5 shows monthly average per unit) production costs for producing Good X.
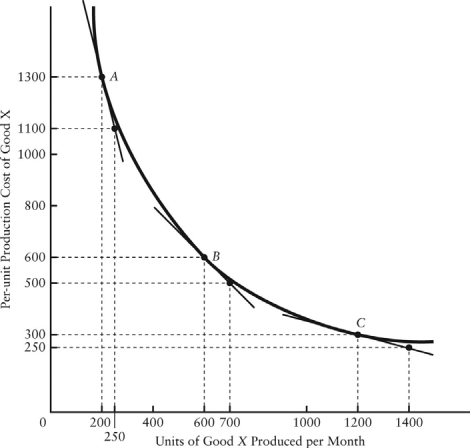 FIGURE 2-5
-A basic underlying point in economics is that
FIGURE 2-5
-A basic underlying point in economics is that
A) people have unlimited wants in the face of limited resources.
B) there are unlimited resources.
C) governments should satisfy the needs of the people.
D) people have limited wants in the face of limited resources.
E) governments should never interfere in the workings of a market economy.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Andrea has a job that pays her $25 000 per year after taxes) . She is considering quitting her job and going to university full time for four years. Tuition fees and books will cost $12 000 per year. Living expenses in either situation will cost $10 000 per year. What is the opportunity cost of Andreaʹs four -year university degree?
A) $88 000
B) $100 000
C) $120 000
D) $148 000
E) $188 000
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a bakeshop with 5 employees can produce both pies and cakes. In one day, if all resources are devoted to baking pies, the shop can produce 125 pies; if all resources are devoted to baking cakes, the shop can produce 50. What is the shopʹs opportunity cost of producing any one pie?
A) 125 pies
B) 0.4 cakes
C) 2.5 pies
D) 0.4 pies
E) 50 cakes
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is illustrated by the circular flow of income?
A) the flows of expenditures and income in a household
B) that firms own the factors of production
C) the interaction of households and firms through the factors and goods markets
D) that the flow of payments moves in the same direction as the flow of goods
E) that there is no relationship between goods markets and factor markets
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-5 shows monthly average per unit) production costs for producing Good X.
 FIGURE 2-5
-Which of the following best describes the study of economics?
FIGURE 2-5
-Which of the following best describes the study of economics?
A) how to plan an economy
B) how to limit human wants so that scarce resources are sufficient
C) why resources are scarce
D) the allocation of scarce resources among alternative uses
E) how to distribute income as equally as possible
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most modern economies in the world today
A) have pure market exchange.
B) are similar to feudal systems.
C) are mostly run by government decree.
D) have a mix of traditional, command and market elements.
E) are complex systems that defy description and analysis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
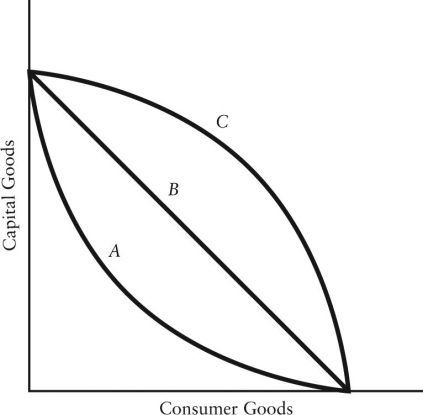 FIGURE 1-5
-Refer to Figure 1-5. Which production possibilities boundaries are consistent with increasing opportunity costs?
FIGURE 1-5
-Refer to Figure 1-5. Which production possibilities boundaries are consistent with increasing opportunity costs?
A) boundary A only
B) boundaries A and B
C) boundary C only
D) boundaries B and C
E) boundaries A, B, and C
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has most contributed to the globalization of the economy?
A) the decreased importance of agriculture
B) reductions in transportation and communication costs
C) the shift toward a market economy in China
D) tariffs and trade barriers
E) the decline in the relative importance of manufacturing
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Money facilitates trade and specialization by
A) allowing an efficient barter system to develop.
B) increasing the value of gold.
C) eliminating the need for barter.
D) reducing the shift of resources between uses.
E) providing employment for coin makers.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a budget of $200 million, the government can choose to purchase 4 helicopters or repair 200 km of highway.
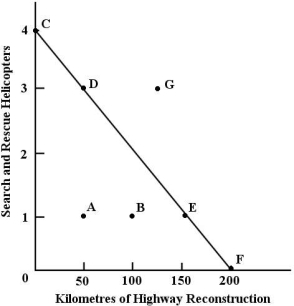 FIGURE 1-1
-Refer to Figure 1-1. Which of the following combinations of kilometres of highway repair and helicopters is unaffordable, given the governmentʹs budget of $200 million?
FIGURE 1-1
-Refer to Figure 1-1. Which of the following combinations of kilometres of highway repair and helicopters is unaffordable, given the governmentʹs budget of $200 million?
A) B
B) D
C) E
D) F
E) G
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When discussing types of economic systems the Canadian economy is best described as
A) primarily a public ownership economy.
B) primarily free-market decision making.
C) traditional.
D) a command economy.
E) a mixed economic system.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows two production possibilities boundaries for Country X.
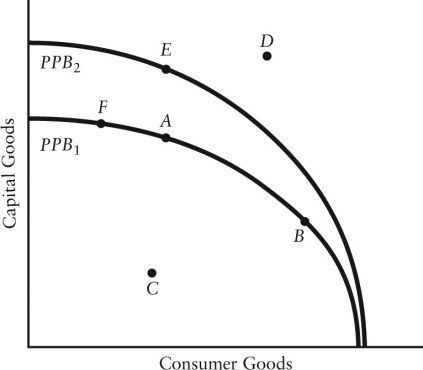 FIGURE 1-4
-Refer to Figure 1-4. If Country X is currently producing at point A, it could move to point B if
FIGURE 1-4
-Refer to Figure 1-4. If Country X is currently producing at point A, it could move to point B if
A) the cost of producing capital goods were to increase.
B) some resources were switched from the capital goods industries to the consumer goods industries.
C) the cost of producing consumer goods were to increase.
D) some resources were switched from the consumer goods industries to the capital goods industries.
E) Country X is no longer able to produce the quantity of capital goods at point A.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below illustrates that, in one day, Tristan can produce either 12 fishing lures or mow 3 lawns, while Thomas can produce either 6 fishing lures or mow 6 lawns.  TABLE 1-1
-Refer to Table 1-1. If Tristan and Thomas want to maximize their joint output from one day of work, how should they specialize their production?
TABLE 1-1
-Refer to Table 1-1. If Tristan and Thomas want to maximize their joint output from one day of work, how should they specialize their production?
A) Tristan produces 3 mowed lawns; Thomas produces 6 mowed lawns
B) Tristan produces 6 lures; Thomas produces 6 lures
C) Tristan produces 6 lures and 3 mowed lawns
D) Tristan produces 12 lures; Thomas produces 6 mowed lawns
E) Tristan produces nothing, Thomas produces 6 lures and 6 mowed lawns
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a budget of $200 million, the government can choose to purchase 4 helicopters or repair 200 km of highway.
 FIGURE 1-1
-Refer to Figure 1-1. For the government, the opportunity cost of one search and rescue helicopter is
FIGURE 1-1
-Refer to Figure 1-1. For the government, the opportunity cost of one search and rescue helicopter is
A) 0 kilometres of highway repair.
B) 50 kilometres of highway repair.
C) 100 kilometres of highway repair.
D) 150 kilometres of highway repair.
E) 200 kilometres of highway repair.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a budget of $200 million, the government can choose to purchase 4 helicopters or repair 200 km of highway.
 FIGURE 1-1
-Refer to Figure 1-1. If the government chooses to allocate all $200 million to highway repair, we can say that
FIGURE 1-1
-Refer to Figure 1-1. If the government chooses to allocate all $200 million to highway repair, we can say that
A) the opportunity cost of the highway repair is uncertain.
B) the opportunity cost of the highway repair is $0.
C) the opportunity cost of the highway repair is 4 search and rescue helicopters.
D) there is no opportunity cost involved because the government has achieved its objectives.
E) there is no opportunity cost involved because the government stayed within its budget.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows two production possibilities boundaries for Country X.
 FIGURE 1-4
-Refer to Figure 1-4. A shift of the production possibilities boundary from PPB1 to PPB2 implies
FIGURE 1-4
-Refer to Figure 1-4. A shift of the production possibilities boundary from PPB1 to PPB2 implies
A) a movement from full employment to some unemployment.
B) that if point E is the new choice of outputs, productivity has increased in the consumer goods industry.
C) that technology in the capital goods industries has improved.
D) an inevitable decrease in total output.
E) that technology in the consumer goods industry has improved.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The downward-sloping line in the diagram below shows the combinations of health care and education expenditures that the government can afford with a given amount of tax revenue.
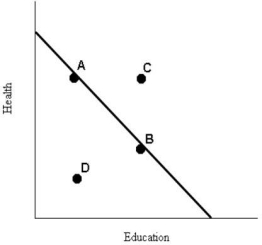 FIGURE 1-6
-Suppose there are only two goods produced in our economysnowplows and helicopters. If there is always a two-for-one tradeoff between the production of these two goods in terms of opportunity cost) , then the production possibilities boundary between snowplows and helicopters is
FIGURE 1-6
-Suppose there are only two goods produced in our economysnowplows and helicopters. If there is always a two-for-one tradeoff between the production of these two goods in terms of opportunity cost) , then the production possibilities boundary between snowplows and helicopters is
A) a downward-sloping curve convex to the origin.
B) circular.
C) a downward-sloping straight line.
D) a downward-sloping straight line with slope equal to -1.
E) a downward-sloping curve concave to the origin.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In mixed economies, economic behaviour is
A) largely determined by a central authority.
B) based primarily on custom and habit.
C) directed only by self interest.
D) affected by elements of tradition, government command, and market incentives.
E) random and unpredictable.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 130
Related Exams