A) As the number of planktonic, photosynthetic organisms available decreases due to increased predation, fewer symbionts are available for the corals to associate with.
B) As pollutants and global temperatures continue to rise, corals will have more difficulty manufacturing the photosynthetic pigments they need to produce their own food.
C) As the number of pollutants dumped into the world's oceans increases, more and more corals will use symbionts that are not photosynthetic.
D) As global temperatures continue to rise, corals will expel more of their colourful, photosynthetic symbionts.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The text describes four ways, or tactics, of feeding. Which of the following is NOT one of those ways?
A) suspension feeding
B) herbivory feeding
C) deposit feeding
D) food- mass feeding
E) fluid feeding
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following objects most closely resembles the pattern of the tube- within- a- tube body plan?
A) a bowling ball with finger holes drilled)
B) a pipe with a straw inside
C) a soda can with the tab removed
D) a cup with a straw in it
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comb jellies may not be the most familiar animal to you, but they are critical in the food chain because they make up a significant portion of the planktonic biomass. Their feeding strategy is predatory and involves adhesives or mucous on their tentacles or other body parts. What feeding tactic do these animals use?
A) suspension feeder
B) fluid feeder
C) food- mass feeder
D) deposit feeder
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you think of the tube- within- a- tube body plan as a pipe with a straw inside, where would you expect to find most of the ectodermal, mesodermal, and endodermal germ layers, respectively?
A) straw; space between pipe and straw; pipe
B) pipe; straw; space inside of straw
C) space inside of straw; straw; space between pipe and straw
D) pipe; space between pipe and straw; straw
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about sponges? Sponges
A) have feeding cells called spicules.
B) have a nerve net but not a central nervous system.
C) have larvae that are motile and move via the motion of cilia.
D) are the simplest diploblastic animals.
E) exhibit bilateral symmetry.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reproductive strategy is facilitated by i.e. is easier to use in) an aquatic habitat, as compared with a terrestrial habitat?
A) asexual reproduction
B) external fertilization
C) internal fertilization
D) viviparity
E) sexual reproduction
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would an adult animal that possesses bilateral symmetry most likely be?
A) triploblastic
B) a coelomate
C) a deuterostome
D) diploblastic
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you came across a novel organism you suspected belonged to one of the following animal phyla: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, or Acoelomorpha. Which of the following characteristics would not be helpful in placing the organism into the correct phylum?
A) whether the organism has a coelom
B) the organism's habitat
C) the organism's feeding strategy
D) whether the organism has a gut
E) whether adults are sessile or motile
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In examining an unknown animal species during its embryonic development, how can you be sure what you are looking at is a protostome and not a deuterostome?
A) There is a well- developed coelom.
B) The mouth develops first, and the anus develops later.
C) There is evidence of cephalization.
D) The animal is triploblastic.
E) The animal is clearly bilaterally symmetrical.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which tissue type, or organ, is not correctly matched with its germ layer tissue?
A) stomach-endoderm
B) skin-ectoderm
C) muscular-mesoderm
D) nervous-mesoderm
E) skeletal-mesoderm
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If in the future the current molecular evidence regarding animal origins is further substantiated, what will be true of any contrary evidence regarding the origin of animals derived from the fossil record?
A) The contrary fossil evidence will be seen as a hoax.
B) Phylogenies involving even the smallest bit of fossil evidence will need to be discarded.
C) Only phylogenies based solely on fossil evidence will need to be discarded.
D) The fossil record will henceforth be ignored.
E) The fossil evidence will be understood to have been interpreted incorrectly because it is incomplete.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
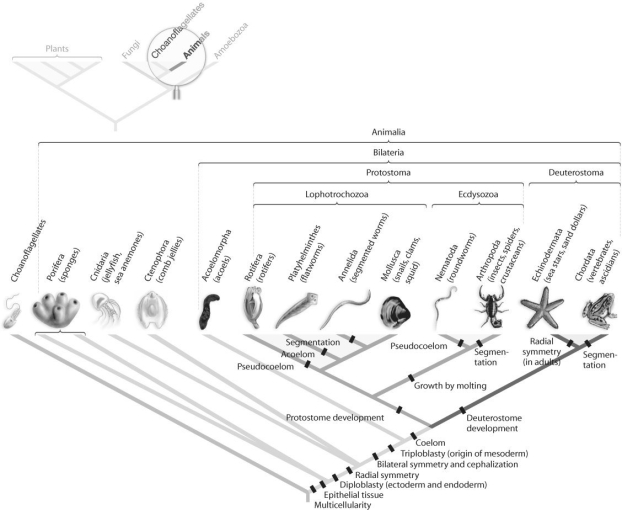 Figure 30.2
-Which morphological trait evolved more than once in animals, according to the phylogeny based on DNA sequence data found in Figure 30.2 above?
Figure 30.2
-Which morphological trait evolved more than once in animals, according to the phylogeny based on DNA sequence data found in Figure 30.2 above?
A) bilateral symmetry
B) coelom
C) protostome development
D) segmentation
E) tissue
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While looking at some seawater through your microscope, you spot the egg of an unknown animal. Which of the following tests could you not use to determine whether the developing organism is a protostome or a deuterostome?
A) See whether the coelom is formed from a split in the mesoderm or from mesodermal pockets pinched off the gut.
B) See whether the animal exhibits spiral cleavage or radial cleavage during early development.
C) See whether the pore formed during gastrulation becomes the mature animal's mouth or its anus.
D) See whether the ectoderm forms the mature animal's skin/exoskeleton or nervous system.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use Figure 30.3 and the following information when answering the next question.
In a review paper published in 2000, Adoutte et al. examined some animal phylogenies generated by comparing the ribosoma rRNA) of animals from many different phyla. They then integrated these independently created phylogenies into one phylog best fit all the data.
Figure 30.4 compares a traditional phylogeny based on morphological characteristics A) to the new molecular- based phylog described by Adoutte et al. B) .
Note that platyhelminthes, nemerteans, and entoprocts, which do not have coeloms and are classified as acoelomates in the morphological phylogeny, are reclassified as lophotrochozoans in the molecular phylogeny. Similarly, groups classified as pseudocoelomates in the morphological phylogeny are reclassified as either lophotrochozoans or ecdysozoans in the molecula phylogeny; other lophotrochozoans and ecdysozoans have coeloms.
A. Adoutte, G. Balavoine, N. Lartillot, O. Lespinet, B. Prud'homme, and R. de Rosa. 2000. The new animal phylogeny.
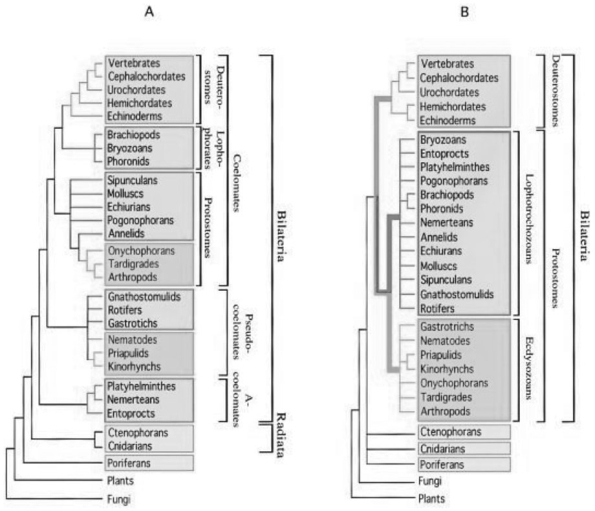 Figure 30.3
-What does this reclassification based on molecular data imply about the evolution of acoelomates, pseudocoelomates, and coelomates?
Figure 30.3
-What does this reclassification based on molecular data imply about the evolution of acoelomates, pseudocoelomates, and coelomates?
A) Pseudocoelomates can be seen as an intermediate stage between acoelomate and coelomate development.
B) Some pseudocoelomates and acoelomates have evolved from coelomates.
C) Although acoelomates and pseudocoelomates evolved only once, coelomates evolved multiple times in different lineages.
D) Only the animals that evolved earliest are acoelomates.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose all of the suspension feeders were removed from a lake. What would you expect to happen after a brief period of time?
A) The water would become murkier.
B) The water would become clearer.
C) The water would remain the same.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bilateral symmetry is advantageous primarily because it allows for the development of
A) duplicate body parts in case of injury.
B) limbs for the infant to attach to a parent.
C) a specialized head and posterior.
D) a specialized body cavity.
E) a hydrostatic skeleton.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which feeding tactic is most associated with a large- toothed, predatory carnivore?
A) suspension feeder
B) deposit feeder
C) fluid feeder
D) food- mass feeder
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Parasitism is one of the most successful life strategies ever to evolve. Which of the following is consistent with this finding?
A) Parasites do not generally kill their hosts, thus they can feed on the same host throughout the host's normal life span and do not have competition from decomposers.
B) Parasites, unlike predators, feed on almost all the tissues of their host.
C) Parasites generally kill their host and can feed for a very long time because they are much smaller than their host.
D) Parasites almost always predigest their hosts' tissues and, therefore, spend less energy and require fewer structural adaptations.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Limbs-especially jointed limbs-are an important evolutionary development because they allow animals to
A) undergo complete metamorphosis.
B) have young disperse from sessile adults.
C) develop an endoskeleton.
D) move quickly and precisely.
E) inhabit aquatic environments.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 42
Related Exams