A) Rate = k[A]
B) Rate = k[B]
C) Rate = k[A][B]
D) Rate = k[A][B]2
E) Rate = k[A]2[B]
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A second-order reaction starts with an initial concentration of 0.100 mol/L of the reactant.If the rate constant is 1.4 × 10-2 L/mol·s,what is the time required to decrease the initial concentration to 0.050 mol/L? 2A → B Rate = k[A]2
A) 710 s
B) 1100 s
C) 49.5 s
D) 3.57 s
E) 2100 s
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw the reaction coordinate diagram for an exothermic reaction involving three mechanistic steps.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the exothermic combustion of coal.Which of the following could increase the rate of reaction?
A) Using smaller pieces of coal
B) Increasing the concentration of oxygen
C) Lowering the temperature
D) Both a and b are correct.
E) None of these
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following proposed mechanism.If this mechanism for the overall reaction were correct,and if k1 were much less than k2,then the observed rate law would be 2A ![Consider the following proposed mechanism.If this mechanism for the overall reaction were correct,and if k<sub>1</sub> were much less than k<sub>2</sub>,then the observed rate law would be 2A C + I I + B C + D A) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A] B) rate = k<sub>2</sub>[I][B] C) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup> D) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup> − k<sub>2</sub>[C][D] E) rate = k<sub>1</sub>k<sub>2</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup>[I][B]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7480/11eac9a9_4bc7_c2fa_acc3_a3444a663318_TB7480_11.jpg) C + I
I + B
C + I
I + B ![Consider the following proposed mechanism.If this mechanism for the overall reaction were correct,and if k<sub>1</sub> were much less than k<sub>2</sub>,then the observed rate law would be 2A C + I I + B C + D A) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A] B) rate = k<sub>2</sub>[I][B] C) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup> D) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup> − k<sub>2</sub>[C][D] E) rate = k<sub>1</sub>k<sub>2</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup>[I][B]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7480/11eac9a9_4bc7_c2fb_acc3_f31debf3e410_TB7480_11.jpg) C + D
C + D
A) rate = k1[A]
B) rate = k2[I][B]
C) rate = k1[A]2
D) rate = k1[A]2 − k2[C][D]
E) rate = k1k2[A]2[I][B]
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Arrhenius equation, 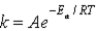 expresses the dependence of the rate constant on the reaction temperature.The slope of a plot of ln(k) versus 1/T is equal to
expresses the dependence of the rate constant on the reaction temperature.The slope of a plot of ln(k) versus 1/T is equal to
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a reaction coordinate diagram,reacting molecules are most unstable ______.
A) at their initial position
B) when they are about to collide
C) right after they collide
D) at the transition state
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct for the first-order reaction: A → 2B?
A) The concentration of A decreases linearly with respect to time.
B) The concentration of A is constant with respect to time.
C) The natural logarithm of the concentration of A decreases linearly with respect to time.
D) The rate of reaction is constant with respect to time.
E) The rate constant,k,of the reaction decreases linearly with respect to time.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Molecules must overcome a barrier called the activation energy if they are to react.The highest energy point reached during the progress of a reaction is called the ____.
A) rate determining step
B) transition state
C) half-life
D) elementary step
E) intermediate state
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction A → B + C,which of the following equations corresponds to the integrated expression for a second-order decomposition reaction?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate constant of a first-order decomposition reaction is 0.0147 s-1.If the initial concentration of reactant is 0.178 M,what is the concentration of reactant after 30.0 seconds?
A) 8.72 × 105 M
B) 0.0645 M
C) 0.115 M
D) 0.0785 M
E) 0.643 M
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate constant for a reaction at 40.0°C is exactly 6 times that at 20.0°C.Calculate the Arrhenius energy of activation for the reaction.(R = 8.314 J/K⋅mol)
A) 6.00 kJ/mol
B) 8.22 kJ/mol
C) 68.3 kJ/mol
D) 14.9 kJ/mol
E) none of these
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Radioactive isotopes decay by ________-order kinetics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A catalyst ____.
A) is used up in a chemical reaction
B) changes the potential energy change of the reaction
C) is always a solid
D) does not influence the reaction in any way
E) changes the activation energy of the reaction
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The decomposition of phosphine,PH3,follows first-order kinetics. 4 PH3(g) → P4(g) + 6 H2(g) The half-life for the reaction at 550 °C is 81.3 seconds.What percentage of phosphine remains after 195 seconds?
A) 2.2%
B) 9.8%
C) 19%
D) 42%
E) 58%
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the overall reaction A + 2B → C,which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B]
A) A + B ![]() I (fast)
I (fast)
I + A → C (slow)
B) A + B → I (slow)
I + B → C (fast)
C) 2B → I (slow)
A + I → C (fast)
D) 2B ![]() I (fast)
I (fast)
I + A → C (slow)
E) A + 2B ![]() I (fast)
I (fast)
I + B → C + B (slow)
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction provided,the rate of disappearance of I-(aq) at a particular time and concentration is 2.4 × 10-3 mol/L·s. IO3-(aq) + 5I-(aq) + 6H+(aq) → 3I2(aq) + 3H2O(l) What is the relative rate of appearance of I2(aq) ?
A) 4.0 × 10-3 mol/L·s
B) 7 × 10-3 mol/L·s..
C) -1 × 10-3 mol/L·s
D) 1 × 10-3 mol/L·s
E) 7 × 10-3 mol/L·s
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The _____ of an elementary step is defined as the number of reactant molecules that come together in a reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen monoxide and carbon dioxide. NO2(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO2(g)
A proposed mechanism for this reaction is
2 NO2(g) ![Nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen monoxide and carbon dioxide. NO<sub>2</sub>(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO<sub>2</sub>(g) A proposed mechanism for this reaction is 2 NO<sub>2</sub>(g) NO<sub>3</sub>(g) + NO(g) (fast,equilibrium) NO<sub>3</sub>(g) + CO(g) → NO<sub>2</sub>(g) + CO<sub>2</sub>(g) (slow) What is a rate law that is consistent with the proposed mechanism? A) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO] [NO]<sup>-1</sup> B) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO] C) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>][CO] D) rate = k[NO<sub>3</sub>][CO] E) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7480/11eac9a9_4bc7_ea0c_acc3_7fa99bedb7c8_TB7480_11.jpg) NO3(g) + NO(g)
(fast,equilibrium)
NO3(g) + CO(g) → NO2(g) + CO2(g)
(slow)
What is a rate law that is consistent with the proposed mechanism?
NO3(g) + NO(g)
(fast,equilibrium)
NO3(g) + CO(g) → NO2(g) + CO2(g)
(slow)
What is a rate law that is consistent with the proposed mechanism?
A) rate = k[NO2]2[CO] [NO]-1
B) rate = k[NO2]2[CO]
C) rate = k[NO2][CO]
D) rate = k[NO3][CO]
E) rate = k[NO2]2
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The decomposition of formic acid follows first-order kinetics. HCO2H(g) → CO2(g) + H2(g) The half-life for the reaction at 550 °C is 24 seconds.How many seconds does it take for the formic acid concentration to decrease by 87.5%?
A) 24 s
B) 36 s
C) 48 s
D) 72 s
E) 96 s
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 72
Related Exams